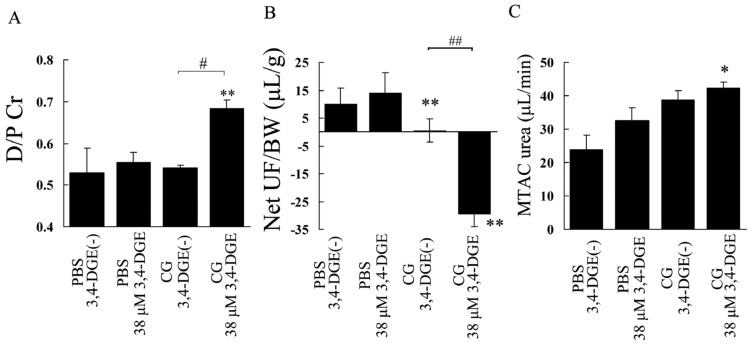
Figure 7.
— Modified peritoneal equilibration test. (A) The creatinine (Cr) concentration in 7% glucose dialysate effluent (D) divided by the Cr concentration in plasma (P) in mice at 2 hours. (B) Net ultrafiltration (UF) / body weight (BW). (C) Mass transfer-area coefficient (MTAC). Compared with mice treated with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) plus 38 μmol/L 3,4-dideoxyglucosone-3-ene (3,4-DGE), mice treated with chlorhexidine gluconate (CG) plus 38 μmol/L 3,4-DGE showed high peritoneal transport. Net UF / BW and MTAC urea indicated that CG treatment induced ultrafiltration failure and high urea transport. Number of mice: PBS without 3,4-DGE [PBS+3,4-DGE(-), n = 3]; PBS+38 μmol/L 3,4-DGE (n = 3); CG+3,4-DGE(-) (n = 3); CG+38 μmol/L 3,4-DGE (n = 5). All values: mean ± standard error of the mean. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 versus PBS-treated mice receiving the same dose of 3,4-DGE; # p < 0.05; ## p < 0.01.