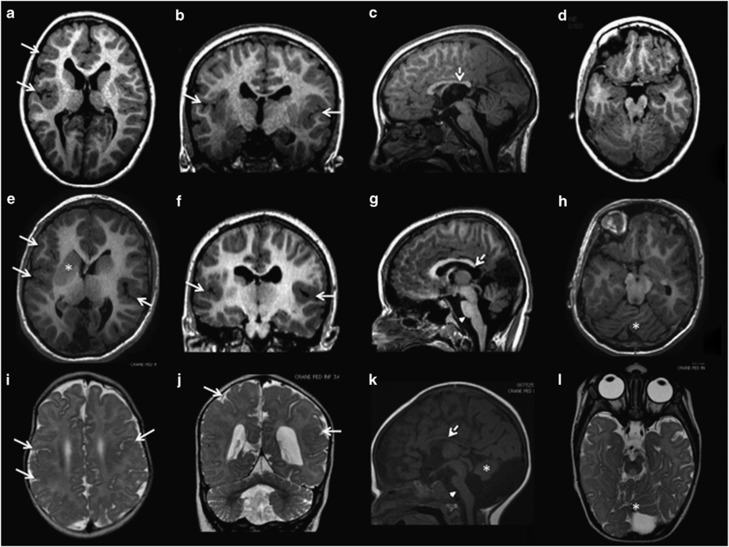
Figure 1.
Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the three patients with TUBA1A mutations. (a–d) Brain MRI of patient 1 at the age of 5 years; (e–h) brain MRI of patient 2 at the age of 11 years; (i–l) brain MRI of patient 3 at the age of 12 months. This figure shows different aspects of PMG in axial (a, e, i) and coronal (b, f, j) sections. All three patients show asymmetrical PMG that appears more prominent in right perisylvian and frontal regions (arrows in a–f). Associated malformations include mild (arrowhead in (g)) or severe brainstem hypoplasia (arrowhead in (k)), vermian dysplasia (asterisks in (h, k and l)), moderate (dotted arrows in (c and g)) or severe hypoplasia of the corpus callosum (dotted arrows in (k)). The basal ganglia are malformed, appearing as large round structures in which the caudate, putamen and globus pallidus cannot be distinguished (asterisks in (e)).