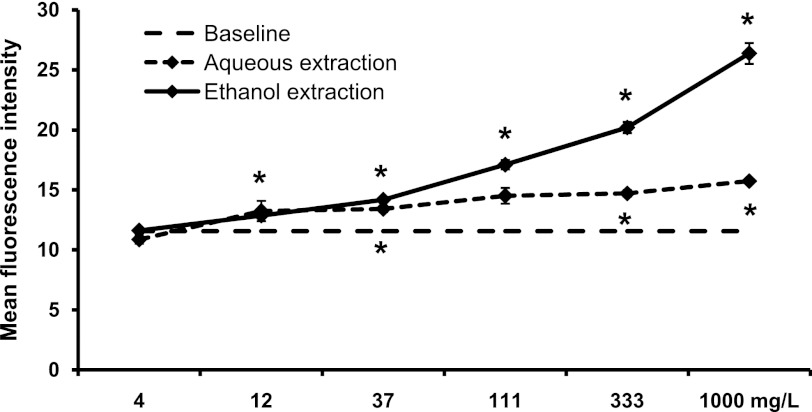
FIG. 7.
Expression of the CD69 activation marker on monocytes. PBMC were cultured for 18 h in the absence (baseline, 11.56±0.30) or presence of either an aqueous extraction or an ethanol extraction from SBLS. The aqueous extract had a minor, but significant effect on monocytes. In contrast, the ethanol extract triggered a significant, dose-dependent increase in expression of the CD69 activation marker on monocytes. Conditions were assayed in triplicate, and the results shown are mean±SD values from a representative of three separate experiments using cells from three different donors.