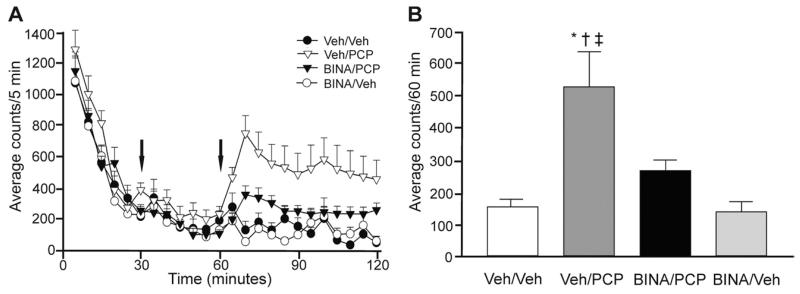
Fig. 2.
BINA suppresses PCP-induced hyperlocomotion in rats. (A) Pretreatment with BINA (32 mg/kg i.p.) 30 min after animals were placed in the open field chamber and 30 min before PCP (5.6 mg/kg i.p.) administration attenuated PCP-induced hyperlocomotor activity. Times of injections (t=30 min for BINA and t=60 min for PCP) are indicated by arrows. (B) The average locomotor activity during the 60 min after PCP administration is significantly higher in the Veh/PCP group than in the Veh/Veh (* P<0.01), BINA/PCP († P<0.01), and BINA/Veh (‡ P<0.01) groups. Data (average counts/60 min) is presented as mean±SEM (n=8–12 per dose group).