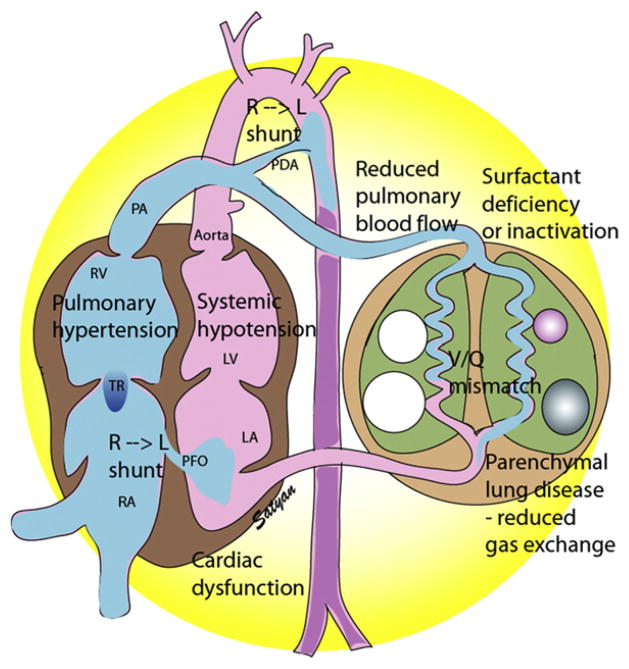
Fig. 4.
Hemodynamic changes in PPHN/HRF. Surfactant deficiency (RDS) or inactivation (MAS or pneumonia) results in parenchymal lung disease and ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) mismatch. Increased PVR results in reduced pulmonary blood flow and right-to-left shunt through the PDA and/or PFO. Pulmonary hypertension, often associated with systemic hypotension, results in septal deviation to the left. Cardiac dysfunction secondary to asphyxia, sepsis, or CDH may contribute to pulmonary venous hypertension and complicate HRF. LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; PA, pulmonary artery; PDA, patent ductus arteriosus; PFO, patent foramen ovale; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle; TR, tricuspid regurgitation. (Copyright © Satyan Lakshminrusimha.)