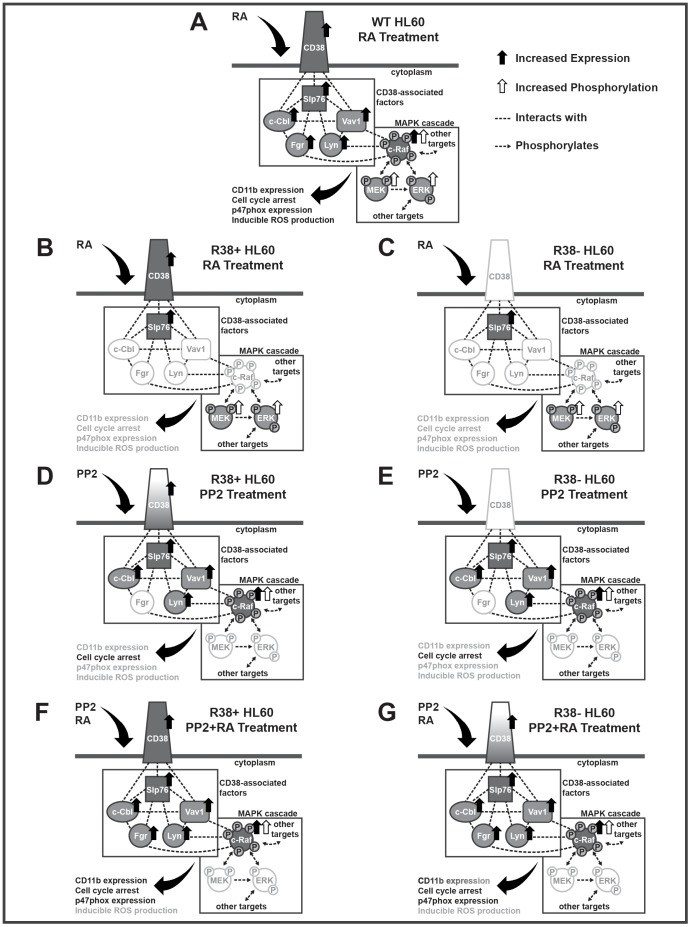
Figure 7. Diagrams of the signaling proteins investigated in this study for each treatment case in R38+ and R38− compared to the RA-treated WT HL60 cells.
For a given protein, solid black arrows indicate increased expression while white arrows indicate increased phosphorylation. Dashed black lines indicate an interaction that has previously been demonstrated in this lab by immunoprecipitation and/or FRET, with the exception of Fgr:Slp76 and Fgr:c-Raf. These two interactions are implied by the known binding of Slp76 and c-Raf to Src-family kinase members. Dashed black lines with arrowheads indicate phosphorylation (kinase) events known in the literature. Solid-filled factors vs. white-filled factors serve to clarify the expression indicated by the black arrows. Gradient-filled factors indicate expression but to a lower level than the RA-treated WT case. Downstream effects (CD11b expression, p47phox expression, etc) are written in black if they occur, grey if they do not occur, or in gradient if they occur but to a lesser extent than the RA-treated WT HL60 case. A: In RA-treated WT HL60, CD38 is upregulated, along with its intracellular binding partners Slp76, Vav1, c-Cbl, and Lyn. Fgr is also upregulated. MEK and ERK show increased phosphorylation, while c-Raf is upregulated and shows increased phosphorylation at S259, S621 and S289/296/301. Differentiation markers that occur include CD11b expression, cell cycle arrest, p47phox expression and inducible ROS production. B: In RA-treated R38+ HL60, CD38 is upregulated, but not Vav1, c-Cbl, or Lyn. Fgr is not upregulated. MEK and ERK show increased phosphorylation; however c-Raf is not upregulated, nor shows increased phosphorylation. Increased CD11b expression, cell cycle arrest, p47phox expression and inducible ROS production do not occur. C: In RA-treated R38− HL60, CD38 is not upregulated, nor Vav1, c-Cbl, or Lyn. Fgr is not upregulated. MEK and ERK show increased phosphorylation; however c-Raf is not upregulated, nor shows increased phosphorylation. Increased CD11b expression, cell cycle arrest, p47phox expression and inducible ROS production do not occur. D: In PP2-treated R38+ HL60, CD38 is partially upregulated (indicated by the gradient CD38), and Slp76, Vav1, c-Cbl, and Lyn are upregulated. Fgr is not upregulated. MEK and ERK phosphorylation is decreased; however c-Raf is upregulated and shows increased phosphorylation. Increased cell cycle arrest occurs, but not increased CD11b expression, p47phox expression or inducible ROS production. E: In PP2-treated R38− HL60, CD38 is not upregulated, but Slp76, Vav1, c-Cbl, and Lyn are upregulated. Fgr is not upregulated. MEK and ERK phosphorylation is decreased; however c-Raf is upregulated and shows increased phosphorylation. Increased cell cycle arrest occurs, but not increased CD11b expression, p47phox expression or inducible ROS production. F: In PP2+RA-treated R38+ HL60, CD38 is upregulated, along with Slp76, Vav1, c-Cbl, and Lyn. Fgr is also upregulated. MEK and ERK phosphorylation is decreased; however c-Raf is upregulated and shows increased phosphorylation. Differentiation markers that occur include CD11b expression, cell cycle arrest, and p47phox expression, but not inducible ROS production. G: In PP2+RA-treated R38− HL60, CD38 is partially upregulated, along with Slp76, Vav1, c-Cbl, and Lyn. Fgr is also upregulated. MEK and ERK phosphorylation is decreased; however c-Raf is upregulated and shows increased phosphorylation. Differentiation markers that occur include partial CD11b expression, cell cycle arrest, and p47phox expression, but not inducible ROS production.