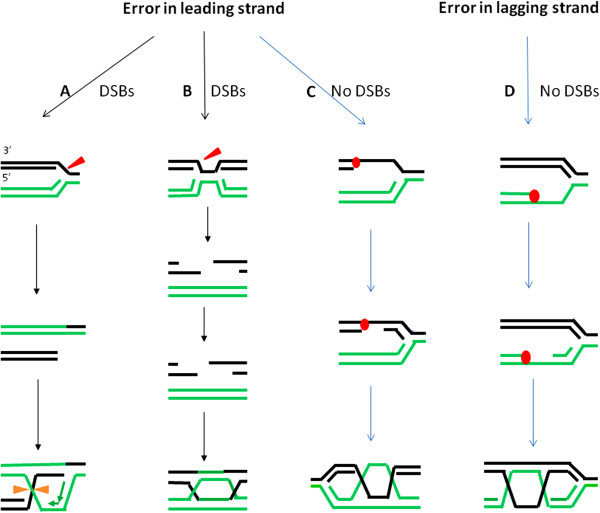
Figure 2.
Pathways of HR repair at stalled/ collapsed replication forks. (A,B,C) Possible pathways resolving leading-strand blockages by HR. Stalled replication forks can be cleaved by an endonuclease to generate a one-sided DSB (A) which can be repaired by HR and re-establishment of a functional fork. Resolution of the single HJ in the orientation shown by the orange arrows results in SCE. Alternatively, a one sided DSBs can be converted into two sided DSBs by encountering a second replication fork; subsequently two end DSBs trigger HR by formation of double HJs (B). Moreover, uncoupling of lagging-strand synthesis can lead to downstream re-initiation of leading strand synthesis, resulting in a leading strand gap, which can be repaired by HR. In this situation, no DSBs are created (C). (D) Possible pathway resolving lagging strand blockage. Downstream re-initiation of lagging-strand synthesis after blockage leaves a gap on the lagging strand which can be repaired by HR.