Fig. 8.
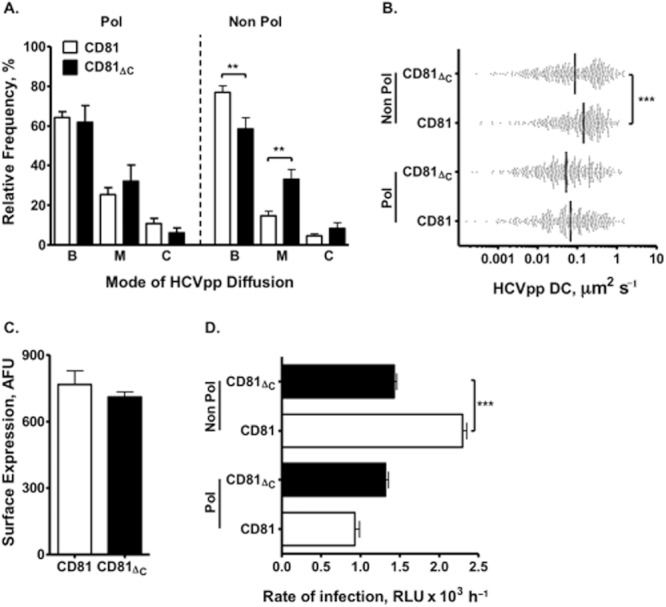
CD81 C-terminal tail regulates HCVpp dynamics and HCV infection. The relative frequency of Brownian (B), mixed (M) or confined (C) HCVpp trajectories on polarized and non-polarized HepG2 cells expressing wild-type (white) and CD81ΔC (black) protein (A). Scatter plots for HCVpp diffusion coefficient (DC) in polarized and non-polarized HepG2 cells expressing wild-type or CD81ΔC are calculated from the MSD-τ plots for Brownian trajectories (B). Each point represents one trajectory with the vertical line indicating the median. A minimum of 10 cells and 250 trajectories were measured per parameter as predetermined by BMC sampling. Non-parametric Mann–Whitney t-tests were used to determine the degree of significance (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.001, ***P < 0.0001). Total and Brownian CD81 DCs are summarized in Table 1. Cell surface expression of wild-type and CD81ΔC in non-polarized HepG2 cells (C). Fifty cells were imaged under the same conditions and the data expressed as arbitrary fluorescence units (AFU). The rate of HCVpp infection of polarized and non-polarized HepG2 cells expressing wild-type and CD81ΔC, where the data are expressed as luciferase relative light units per hour (D). The data are representative of three independent experiments where infections were performed in triplicate. A one-way anova with a Tukey post test was used to determine the degree of significance (***P < 0.0001).
