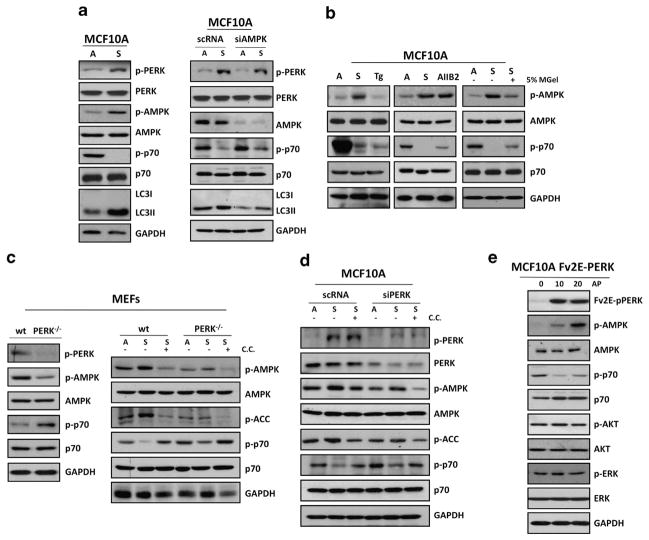
Figure 2.
Adhesion to the ECM prevents PERK-mediated inhibition of mTORC1 signaling via AMPK activation. (a) MCF10A cells grown attached (A) or suspended for 12 h (S; left panel) and transfected with AMPK or control (scRNA) siRNAs (right panel) were lysed and immunoblotted (IB) with indicated antibodies (Abs). (b) Lysates from MCF10A were cultured in attached (A) or suspended (S) conditions or treated with 10 μM thapsigargin (Tg), 10 μg/ml AIIB2 or 5% matrigel (MGel) and IB with the indicated Abs. (c) Lysates of PERK +/+ and PERK −/− MEFs were collected from attached (left panel) and attached (A) and suspended (S) conditions (right panel), treated with or without 10 μM compound C (C.C.) as indicated and IB against the indicated antigens. (d) MCF10A lysates from attached (A) and in suspended (S) cells that were transfected with PERK or control (scRNA) siRNAs were treated with or without 10 μM CC as indicated and IB against the indicated antigens. (e) Adherent Fv2E-ΔNPERK MCF10A treated with or without 100 pM AP were collected at the indicated time points (minutes) and analyzed by IB with the indicated Abs.