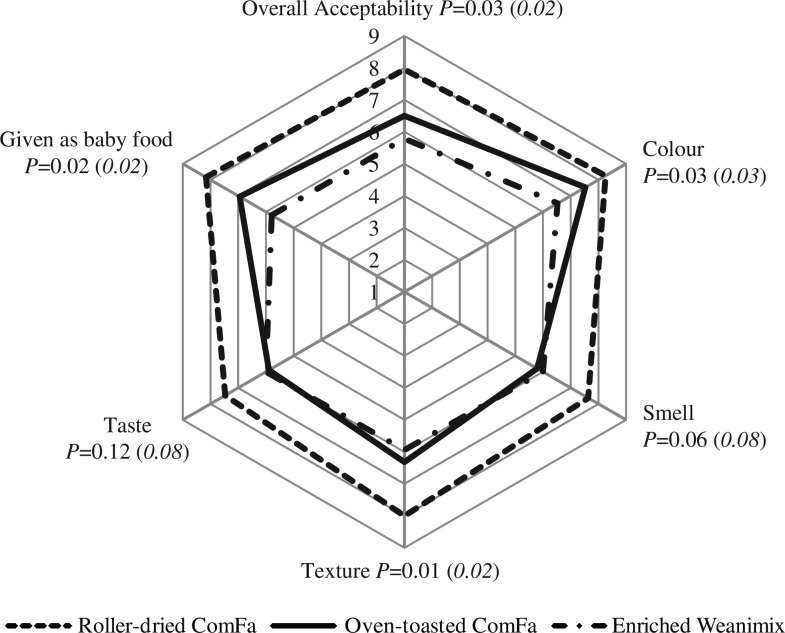
Fig. 3.
Diagrammatic presentation of product liking for sensory attributes and choice to give the formulations as complementary food to infants by 20 female sensory participants.
Sensory attribute with P<0.05 indicates that significant difference among the complementary foods; italicised value in parenthesis is asymptotic significance from Kruskal–Wallis test.
A 9-point hedonic scale was used (1 = least acceptable/dislike extremely; 5 = neutral; 9 = highly acceptable/like extremely) for all attributes except for willingness to give product to babies (1 = not likely; 5 = neutral; 9 = very likely).