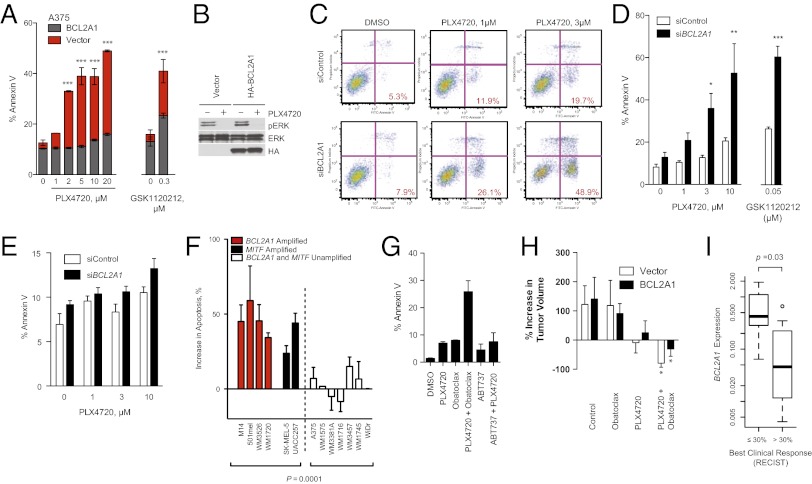
Fig. 5.
BCL2A1 and MITF mediate resistance to BRAF-directed therapy. (A) BRAF-mutant A375 melanoma cells with overexpressed BCL2A1 were treated with PLX4720 or GSK1120212 and apoptosis was measured by Annexin V staining after 48 h of drug treatment. (B) Effect of BCL2A1 overexpression on ERK signaling after 4 h of treatment with 3 µM PLX4720. (C) Effect of concomitant BCL2A1 suppression by siRNA and PLX4720 in BCL2A1 amplified cell line, M14. Quantification of three independent experiments is shown in D. (E) Effect of siBCL2A1 and PLX4720 in BRAF-wild-type (15q-unamplified) cell line MeWo. (F) Effect of siBCL2A1 and PLX4720 (3 µM) on apoptosis in cell lines and short-term cultures. WDir is a colon cancer cell line with BRAF V600E mutation. (G) Effect of obatoclax (100 nM), ABT-737 (1 µM), and PLX4720 (3 µM) on apoptosis of BCL2A1-amplified cell line 501mel after 48 h of treatment. (H) Effect of PLX4720 alone or in combination with obatoclax in mouse xenotransplants. A375 cells expressing BCL2A1 or control vector (five biological replicates each) were injected into mice. Treatment of mice began 12 d after implantation, and tumor volume was measured at baseline and on the 12th d of treatment. *P < 0.05 compared with control. (I) Box-whisker plot comparing BCL2A1 mRNA expression in melanomas from patients before treatment with vemurafenib or GSK1120212 + GSK2118436 (SI Appendix, Table S4). Normalized expression (arbitrary units) was compared in patients who achieved objective responses by standard RECIST criteria (n = 12) versus those without objective responses (n = 7).