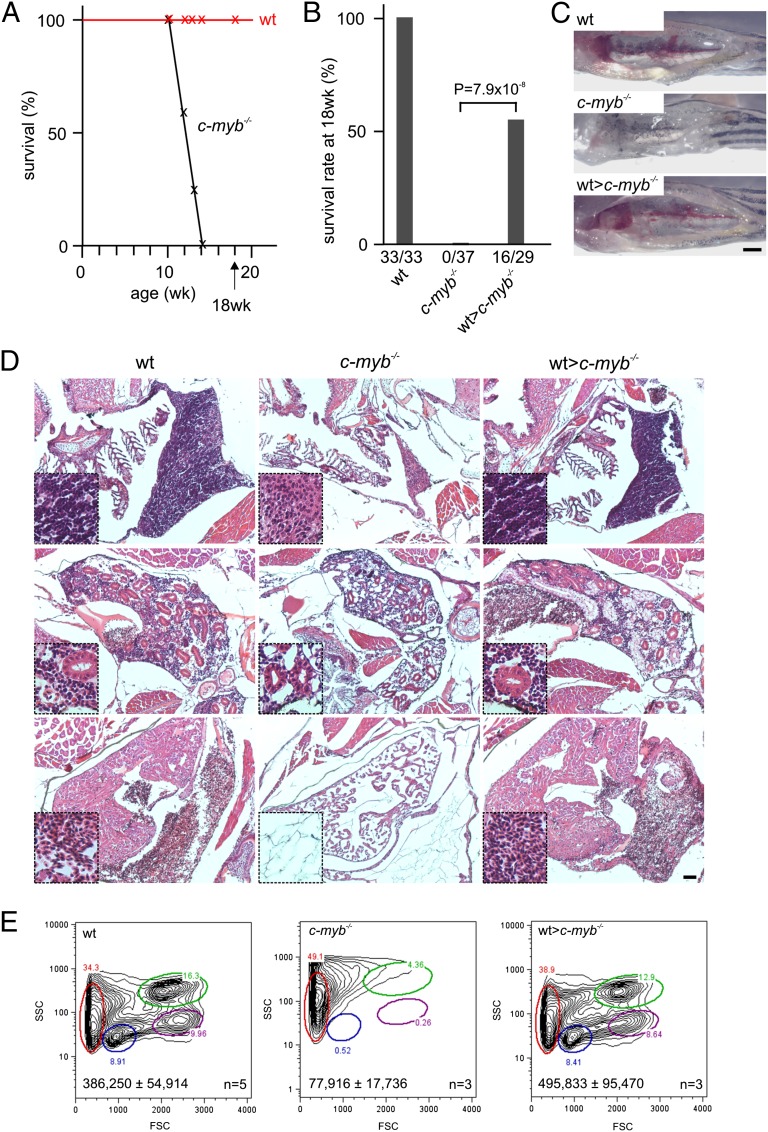
Fig. 1.
Reconstitution of the c-myb−/− mutant phenotype. (A) Survival of wild-type (n = 33) and c-myb−/− mutant (n = 37) fish; mutants do not survive longer than 14 wk of age. (B) Survival rates of wild-type, c-myb−/− mutants and mutant recipients transplanted with wild-type WKM (wt>c-myb−/−) transgenic for an ikaros:eGFP reporter assessed at 18 wk of age. All deaths occurring within the first 24 h after transplantation were considered to be procedural and thus not used for the calculation of survival rates. (C) Macroscopic appearance of head kidneys in wild-type, c-myb−/− mutants and transplanted mutant recipients; note that mutant kidney shows a complete lack of hematopoietic cells (17). (Scale bar, 1 mm.) (D) Hematoxylin/eosin staining of sections through the region of the thymus (Top), kidney (Middle), and heart (Bottom) of wild-type, c-myb−/− mutants and transplanted recipients at 9 wk of age (i.e., 3 wk after transplantation); insets are at fourfold higher magnifications. Note the lack of hematopoietic cells in the mutants and complete hematopoietic reconstitution in transplanted recipients. (Scale bar, 50 μm.) (E) Flow cytometric analyses of WKM cells of wild-type, c-myb−/− mutants and transplanted recipients as in D. FSC, forward light scatter; SSC, side light scatter. Circles denote different blood cell populations in adult wild-type fish: red, erythrocytes; blue, lymphocytes; magenta, precursors; green, myelomonocytes. Total cell numbers (mean± SD) in WKM preparations are indicated.