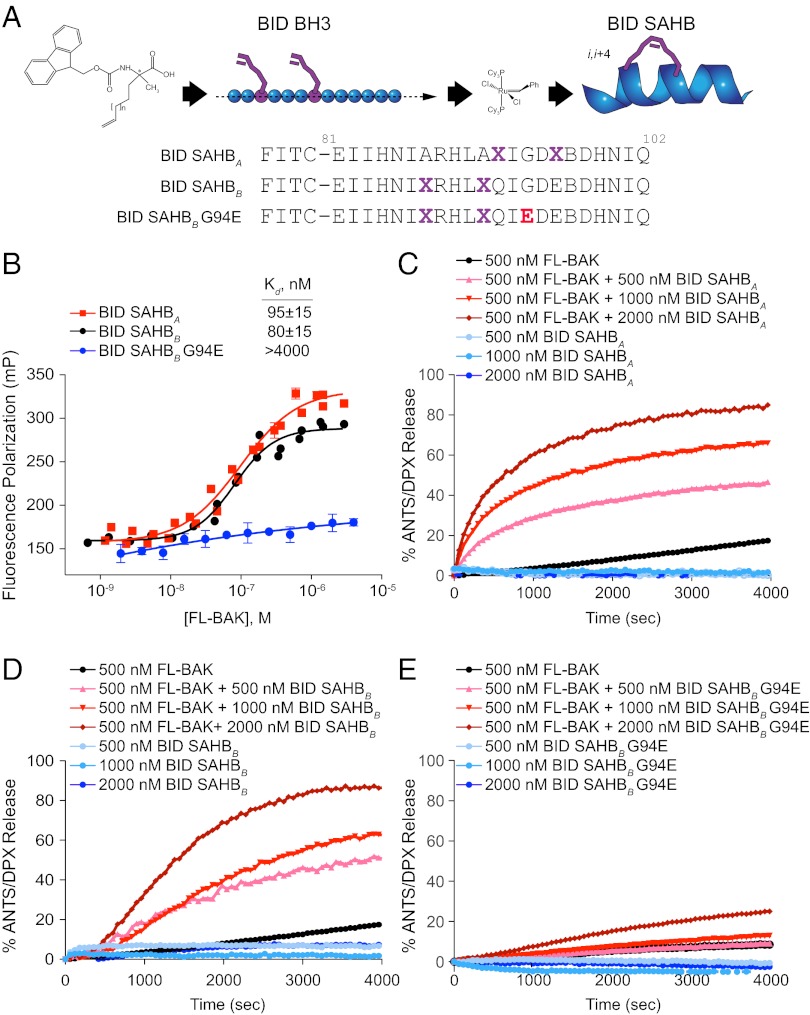
Fig. 3.
BID SAHBs bind to FL-BAK in a sequence-dependent manner and directly trigger FL-BAK activation. (A) SAHBs corresponding to the BH3 motif of the BH3-only protein BID were generated by substituting nonnatural amino acids bearing olefin tethers at i, i+4 positions followed by ruthenium-catalyzed olefin metathesis. G94E point mutagenesis of the hydrophobic binding interface yielded a negative control SAHB for biochemical studies. X, stapling amino acid; B, norleucine (substituted for methionine to avoid thioether-based interference with ruthenium catalysis). (B) BID SAHBs A and B bound to FL-BAK with nanomolar affinity, whereas G94E point mutagenesis abrogated the interaction, as measured by FP assay. Experiments were performed at least in duplicate and were repeated three times with independent preparations of FL-BAK. Data are mean ± SEM. (C–E) BID SAHBs A and B dose-responsively induced FL-BAK–mediated liposomal release of entrapped fluorophore, whereas BID SAHBB G94E, or BID SAHBs or FL-BAK alone, had little to no effect. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments with similar results.