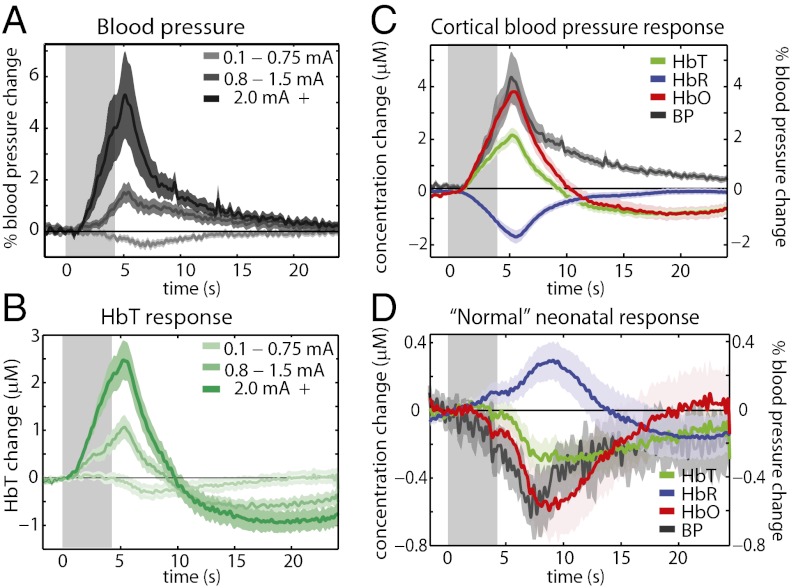
Fig. 1.
Blood pressure effects on the neonatal hemodynamic response. (A) Systemic blood pressure recordings from a femoral arterial line in P12–P13 rats undergoing 4-s, 3-Hz hindpaw stimulation of different amplitudes (n = 7 rats, averaging 33, 30, and 26 runs for low-to-high stimulus amplitudes, respectively). (B) Cortical HbT responses recorded in the same groups as in A. Average P12–P13 cortical hemodynamic response from runs in which systemic blood pressure increases were observed (C) (n = 7 rats, 43 runs), and average P12–P13 cortical hemodynamic response from runs in which systemic blood pressure increases were not observed (D) (n = 7 rats, 46 runs), both overlaid with corresponding average systemic blood pressure response.