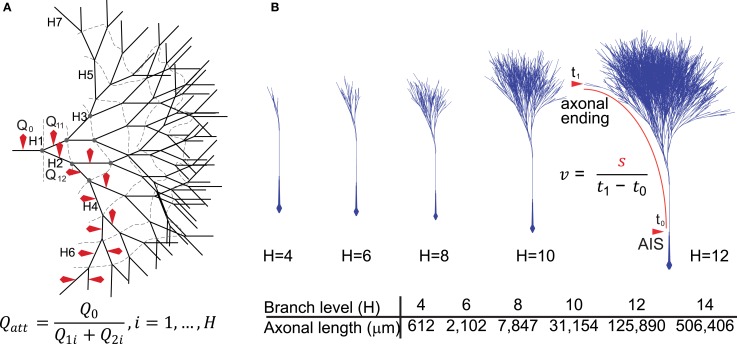
Figure 1.
Diagrammatic representation of the model neurons. (A) Two-dimensional representation of the model axon based on the structure of a full binary tree. The branching level is represented by H1–7 (dashed lines represent branch contours or levels) and red markers indicate the axonal branches from where sodium charge (Qx) was sampled and used to derive charge attenuation (Qatt) according to the formula. (B) A three-dimensional representation of the axonal binary tree for neurons with 4–12 levels of branching (H4–H12). For neurons with 14 levels of branches (H = 14), the total axonal length was about 50 cm, possessing 16,384 branches, 8191 nodes and 8192 axonal endings. We included in the models an axonal segment of ~6 mm representing the connection between the axon initial segment in the substantia nigra and the beginning of the arborization in the striatum. Conduction velocity (v) was calculated using the formula in which s represents the length of the axonal path from the axon initial segment to an axonal ending and t1 − t0 represents the time taken for the propagation of the action potential along that path.