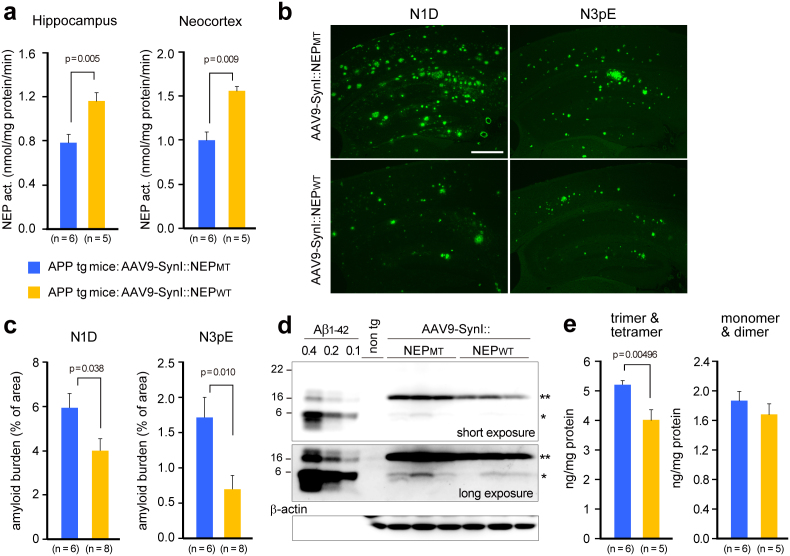
Figure 5. Gene therapeutic effects of NEP gene transfer on Aβ pathologies in the brains.
Seven months after the gene transfer into 15-month-old APP tg mice, brains were removed and analyzed biochemically and immunohistochemically. (a) NEP activities in the hippocampal formation and neocortex. (b) Amyloid burden. Brain sections were immunostained with N-terminal specific antibodies for Aβ (N1D and N3pE, mouse monoclonal). Scale bar, 500 μm. (c) Amyloid load is expressed as percent of the measured area. Data represent mean ± s.e.m. The p values show significant differences between rAAV9-SynI::NEPMT and rAAV-SynI::NEPWT. (d) A representative blot of Aβ and its oligomers. Triton X-100-extractable membrane fractions (20 μg protein) from the hippocampal formation of APP tg mice with rAAV9-NEPMT or rAAV9-NEPWT and non-transgenic (wild type) mice were subjected to western blot analyses using N-terminal specific antibody N1D (rabbit polyclonal). A single asterisk shows Aβ dimer, and a double asterisk shows trimer and tetramer. The blot was reprobed with anti-β-actin antibody. (e) Aβ oligomers in the blots were quantified by densitometry. Synthetic Aβ1-42 (0.1, 0.2, 0.4 ng) run on the same gel as indicated in d was used for calibration within a linear range. The p values show significant differences between rAAV9-SynI::NEPMT and rAAV-SynI::NEPWT. Data represent mean ± s.e.m.