Abstract
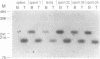
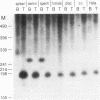
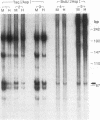
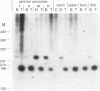
Alu repeats are especially rich in CpG dinucleotides, the principal target sites for DNA methylation in eukaryotes. The methylation state of Alus in different human tissues is investigated by simple, direct genomic blot analysis exploiting recent theoretical and practical advances concerning Alu sequence evolution. Whereas Alus are almost completely methylated in somatic tissues such as spleen, they are hypomethylated in the male germ line and tissues which depend on the differential expression of the paternal genome complement for development. In particular, we have identified a subset enriched in young Alus whose CpGs appear to be almost completely unmethylated in sperm DNA. The existence of this subset potentially explains the conservation of CpG dinucleotides in active Alu source genes. These profound, sequence-specific developmental changes in the methylation state of Alu repeats suggest a function for Alu sequences at the DNA level, such as a role in genomic imprinting.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batzer M. A., Deininger P. L. A human-specific subfamily of Alu sequences. Genomics. 1991 Mar;9(3):481–487. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90414-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batzer M. A., Kilroy G. E., Richard P. E., Shaikh T. H., Desselle T. D., Hoppens C. L., Deininger P. L. Structure and variability of recently inserted Alu family members. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6793–6798. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besser D., Götz F., Schulze-Forster K., Wagner H., Kröger H., Simon D. DNA methylation inhibits transcription by RNA polymerase III of a tRNA gene, but not of a 5S rRNA gene. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 3;269(2):358–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81193-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickmore W. A., Sumner A. T. Mammalian chromosome banding--an expression of genome organization. Trends Genet. 1989 May;5(5):144–148. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. DNA methylation and the frequency of CpG in animal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 11;8(7):1499–1504. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.7.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. The essentials of DNA methylation. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90526-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H. DNA methylation and gene activity. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90479-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L., Batzer M. A., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. Master genes in mammalian repetitive DNA amplification. Trends Genet. 1992 Sep;8(9):307–311. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90262-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll D. J., Migeon B. R. Sex difference in methylation of single-copy genes in human meiotic germ cells: implications for X chromosome inactivation, parental imprinting, and origin of CpG mutations. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1990 May;16(3):267–282. doi: 10.1007/BF01233363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich M., Gama-Sosa M. A., Huang L. H., Midgett R. M., Kuo K. C., McCune R. A., Gehrke C. Amount and distribution of 5-methylcytosine in human DNA from different types of tissues of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2709–2721. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gama-Sosa M. A., Wang R. Y., Kuo K. C., Gehrke C. W., Ehrlich M. The 5-methylcytosine content of highly repeated sequences in human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3087–3095. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Conkin K. F. Chromatin structure and de novo methylation of sperm DNA: implications for activation of the paternal genome. Science. 1985 May 31;228(4703):1061–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.2986289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett S. K., Reik W. Methylation levels of maternal and paternal genomes during preimplantation development. Development. 1991 Sep;113(1):119–127. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Schmid C. W. Repetitive sequences in eukaryotic DNA and their expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:813–844. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurka J., Milosavljevic A. Reconstruction and analysis of human Alu genes. J Mol Evol. 1991 Feb;32(2):105–121. doi: 10.1007/BF02515383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jüttermann R., Hosokawa K., Kochanek S., Doerfler W. Adenovirus type 2 VAI RNA transcription by polymerase III is blocked by sequence-specific methylation. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1735–1742. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1735-1742.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafri T., Ariel M., Brandeis M., Shemer R., Urven L., McCarrey J., Cedar H., Razin A. Developmental pattern of gene-specific DNA methylation in the mouse embryo and germ line. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):705–714. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochanek S., Renz D., Doerfler W. DNA methylation in the Alu sequences of diploid and haploid primary human cells. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1141–1151. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05755.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu W. M., Schmid C. W. Proposed roles for DNA methylation in Alu transcriptional repression and mutational inactivation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 25;21(6):1351–1359. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.6.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matera A. G., Hellmann U., Hintz M. F., Schmid C. W. Recently transposed Alu repeats result from multiple source genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6019–6023. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matera A. G., Hellmann U., Schmid C. W. A transpositionally and transcriptionally competent Alu subfamily. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5424–5432. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk M., Boubelik M., Lehnert S. Temporal and regional changes in DNA methylation in the embryonic, extraembryonic and germ cell lineages during mouse embryo development. Development. 1987 Mar;99(3):371–382. doi: 10.1242/dev.99.3.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk M., Grant M. Preferential X-chromosome inactivation, DNA methylation and imprinting. Dev Suppl. 1990:55–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzetto-Zimmerman C., Wolgemuth D. J. Methylation of satellite sequences in mouse spermatogenic and somatic DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2807–2822. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford J., Forrester L., Chapman V., Chandley A., Hastie N. Methylation patterns of repetitive DNA sequences in germ cells of Mus musculus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2823–2836. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza C., Peterson A. C., Rossant J., Balling R. Degree of methylation of transgenes is dependent on gamete of origin. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):251–254. doi: 10.1038/328251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C. W. Human Alu subfamilies and their methylation revealed by blot hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5613–5617. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C., Maraia R. Transcriptional regulation and transpositional selection of active SINE sequences. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Dec;2(6):874–882. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80110-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shemer R., Kafri T., O'Connell A., Eisenberg S., Breslow J. L., Razin A. Methylation changes in the apolipoprotein AI gene during embryonic development of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11300–11304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surani M. A., Barton S. C., Norris M. L. Development of reconstituted mouse eggs suggests imprinting of the genome during gametogenesis. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):548–550. doi: 10.1038/308548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain J. L., Stewart T. A., Leder P. Parental legacy determines methylation and expression of an autosomal transgene: a molecular mechanism for parental imprinting. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):719–727. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90330-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. R., Andersen L. B., Saulino A. M., Gregory P. E., Glover T. W., Collins F. S. A de novo Alu insertion results in neurofibromatosis type 1. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):864–866. doi: 10.1038/353864a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinbauer G. F., Behre H. M., Fingscheidt U., Nieschlag E. Human follicle-stimulating hormone exerts a stimulatory effect on spermatogenesis, testicular size, and serum inhibin levels in the gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist-treated nonhuman primate (Macaca fascicularis). Endocrinology. 1991 Oct;129(4):1831–1839. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-4-1831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]