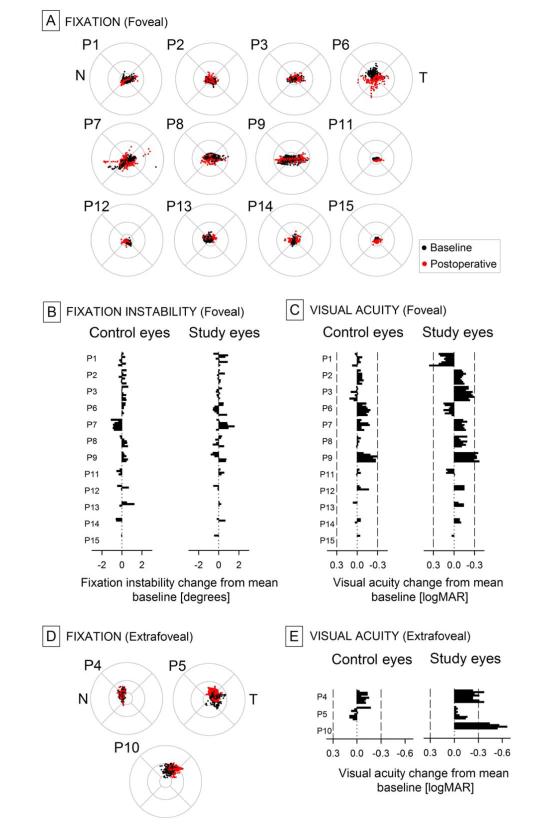
Figure 5.
Retinal location and instability of fixation in RPE65-LCA eyes at baseline and postoperatively, and its relation to changes in visual acuity. A, D, Fixation clouds of all study eyes during a 10 sec epoch recorded while gazing to a 1 deg diameter stationary target adjusted to be visible to each eye. Foveally fixating eyes shown in A and extrafoveally fixating eyes shown in D. Circular patterns show the standard grid centered on the anatomical fovea extending to radii of 1.65, 5 and 10 degrees. All panels are shown in equivalent left retina representation. N and T refer to nasal and temporal retina, respectively. B, Fixation instability values are shown as change from mean baseline values at all postoperative visits in control and study eyes with foveal fixation. VAs are shown as change from mean baseline at all postoperative visits in control and study eyes with foveal (C) or extrafoveal (E) fixation. Limits for 0.30 logMAR (15 letter or 3 line) gain or loss shown with vertical dashed lines.