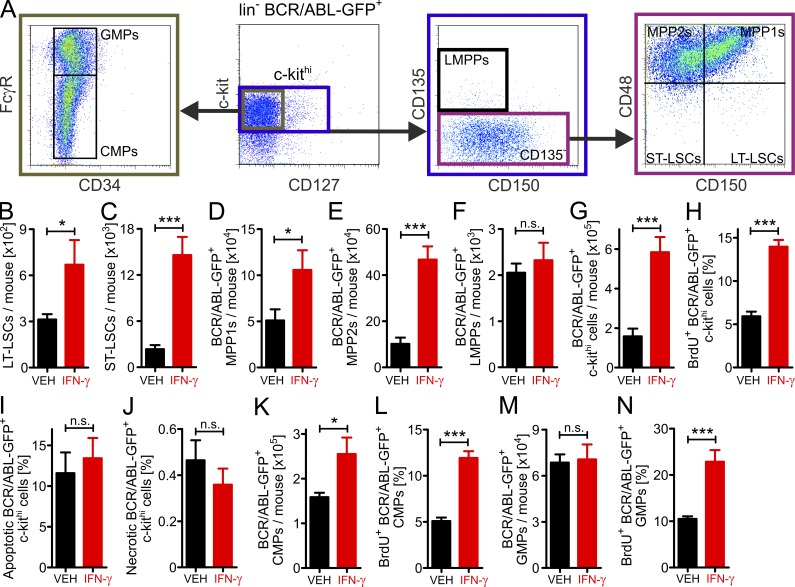
Figure 5.
IFN-γ enhances the proliferation of early LSCs and leukemia progenitor cells in vivo. (A) Gating strategy to identify early LSCs and leukemia progenitor cells in the BM of CML mice. (B–N) BL/6 CML mice were treated with either vehicle (VEH, n = 7) or 2.5 × 105 U of rm-IFN-γ (n = 5) i.p. twice daily on two consecutive days (days 17 and 18 after primary transplantation). On the same days, mice also received BrdU (0.8 mg/ml in drinking water and 1 mg i.p./day). 1 d later, lin−BCR/ABL-GFP+ BM cells were analyzed for LSCs and leukemia progenitor cells. (B) Long-term LSCs (c-kithiCD135−CD48−CD150+). (C) Short-term LSCs (c-kithiCD135−CD48-CD150−). (D) Leukemia MPP1s (c-kithiCD135−CD48+CD150+). (E) Leukemia MPP2s (c-kithiCD135−CD48+CD150−). (F) Leukemia LMPPs (c-kithiCD135+CD150−). (G) Numbers, (H) proliferation, and (I-J) viability of c-kithi leukemia progenitor cells. Numbers (K) and proliferation (L) of leukemia CMPs (c-kithiCD127−CD34+FcγR−). Numbers (M) and proliferation (N) of leukemia GMPs (c-kithiCD127−CD34+FcγR+). Data are displayed as mean ± SEM. Statistics: (B–N) Student’s t test. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.0005. Apoptotic cells, Annexin V+ cells; necrotic cells, AnnexinV+7-AAD+ cells. CMPs, common myeloid progenitors; GMPs, granulocyte-macrophage progenitors; LMPPs, lymphoid-primed multipotent progenitors; LT, long-term; MPPs, multipotent progenitors; ST, short-term.