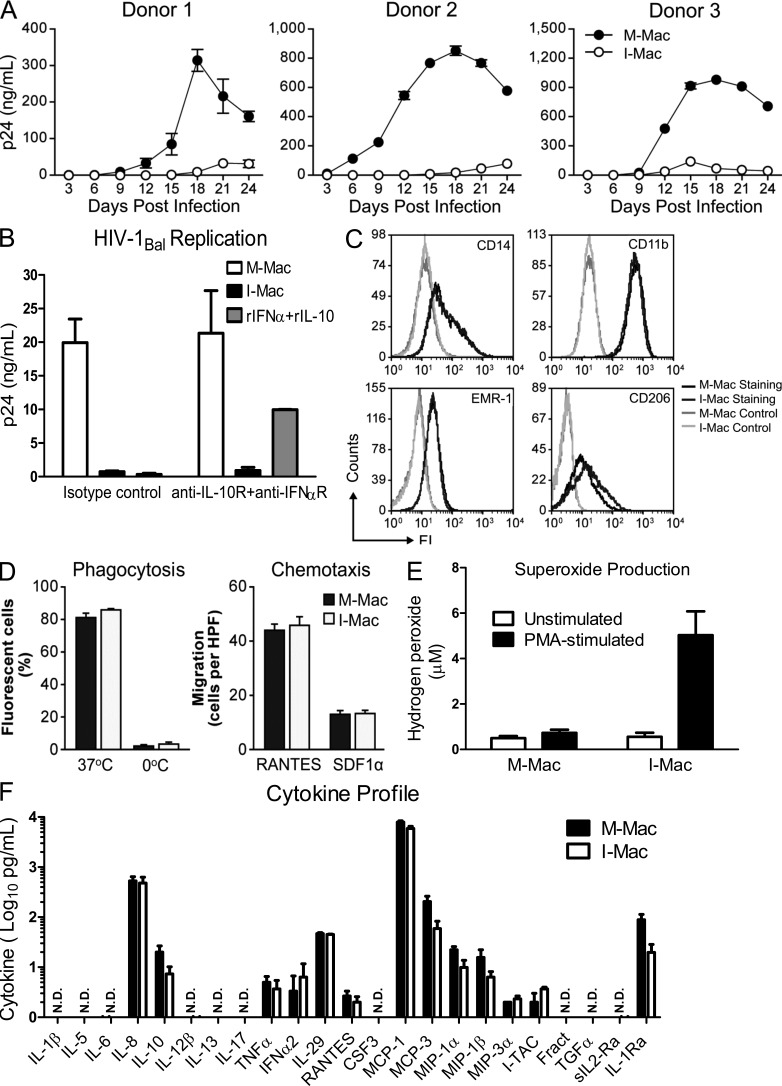
Figure 1.
IL-27 induces macrophages resistant to HIV-1 infection while retaining normal functions and differentiation markers. (A) M-Mac and I-Mac were infected with HIV-1BAL. Viral replication was monitored by measuring p24 antigen in culture supernatants. Results are shown for macrophages cultures obtained from three independent donors and data shown represent mean ± SD of triplicate infection samples. (B) Antibodies that neutralize human IFN-α receptor (10 µg/ml) and IL-10 receptors (10 µg/ml) were kept in culture during the 7-d differentiation of M-Mac and I-Mac. M-Mac and I-Mac differentiated in the presence of neutralizing antibodies were infected with HIV-1Bal, and p24 amount in culture supernatants was measured 14 d after infection. As an additional control to indicate the neutralizing effect, M-Mac differentiated in the presence of neutralizing antibodies were also incubated with recombinant human IFN-α (10 u/ml) and IL-10 (1 ng/ml) for 1 h before HIV-1 infection. Data shown represent means ± SE of three independent experiments. (C) M-Mac and I-Mac were analyzed for CD14, CD11b, EMR-1, and CD206 expression by FACS before infection. (D, left) Phagocytic activities of M-Mac and I-Mac were assessed using a pHrodo dye phagocytosis assay. As a negative control, macrophages were placed on ice to avoid phagocytosis. (right) the migration of M-Mac and I-Mac to RANTES (10 ng/ml) and SDF-1α (100 ng/ml) were assessed by counting cells migrating across filters of microchemotaxis chambers. Data shown represent mean ± SE of three independent experiments. (E) M-Mac and I-Mac were analyzed for superoxide production with or without PMA stimulation. Data shown represent means ± SE of three independent experiments. (F) Supernatants of M-Mac and I-Mac were analyzed for cytokine concentrations using the Multiplex Cytokine assay. Data are shown on a log scale. N.D., not detected. Data shown represent means ± SE of three independent experiments.