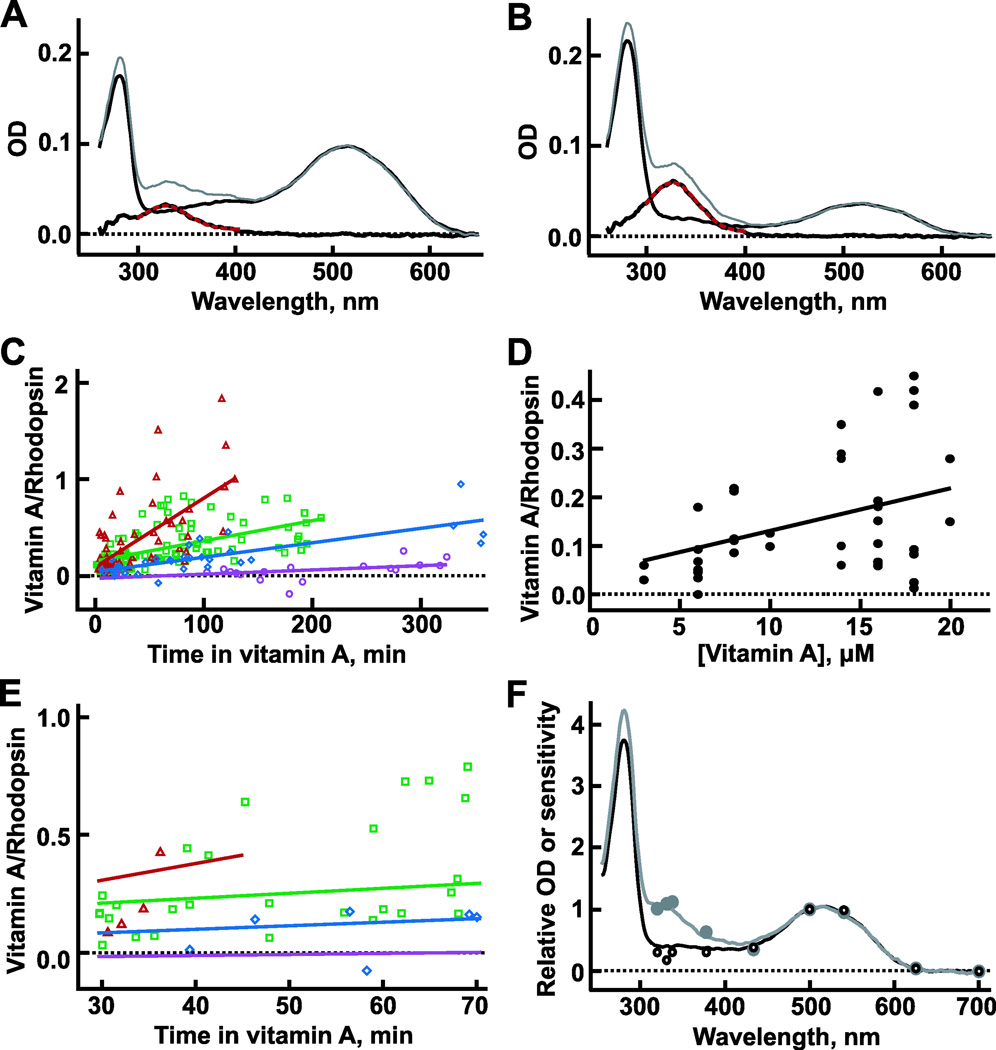
Fig. 4.
Uptake of vitamin A into the outer segments of GS rods. (A) Average OD⊥ spectra before (thin black line) and during treatment with 6 µM vitamin A for 60–90 min (gray line, n = 13 rods). The wavelength maximum of the difference spectrum (thick black line) was 329 nm by fitting with a Gaussian (dashed red line). (B) Corresponding OD∥ measurements for the same cells in (A). The vitamin A to rhodopsin ratio was 0.32, determined from eqn. (2). (C) Time course of vitamin A uptake. Fits by linear regression yielded slopes of 0.000442, 0.00151, 0.00210, 0.00704/min and y-intercepts of −0.0311, 0.0377, 0.146, and 0.101 for bathing concentrations of 1 µM (purple circles and line, n = 19 rods), 3 µM (blue diamonds and line, n = 31 rods), 6–10 µM (green squares and line, n = 98 rods), and 16–20 µM (red triangles and line, n = 54 rods), respectively. T-tests based on the Pearson correlation coefficients for all [vitamin A] yielded P values < 0.02. (D) Increase in initial uptake (treatment time < 15 min) with bathing concentration of vitamin A in 40 rods. The ratio of vitamin A to rhodopsin = 0.0419 + 0.00875[vitamin A], by linear regression, P < 0.005. (E) Time course of vitamin A uptake from 30 to 70 min (from C) during which measurements of sensitivity were made on different cells in physiological recordings. Physiological measurements with more than 17 µM vitamin A were carried out between 30 and 45 min of treatment (cf. red line for 16–20 µM vitamin A). Points and lines reproduce those shown over a longer time scale in (C). (F) Comparison of action spectra from three rods to absorption spectra from eight rods in the presence (gray circles and line) or absence of ~8 µM vitamin A (open circles and black line). The absorption spectrum was adjusted to account for the polarization of the light in the suction electrode recording (see Results).