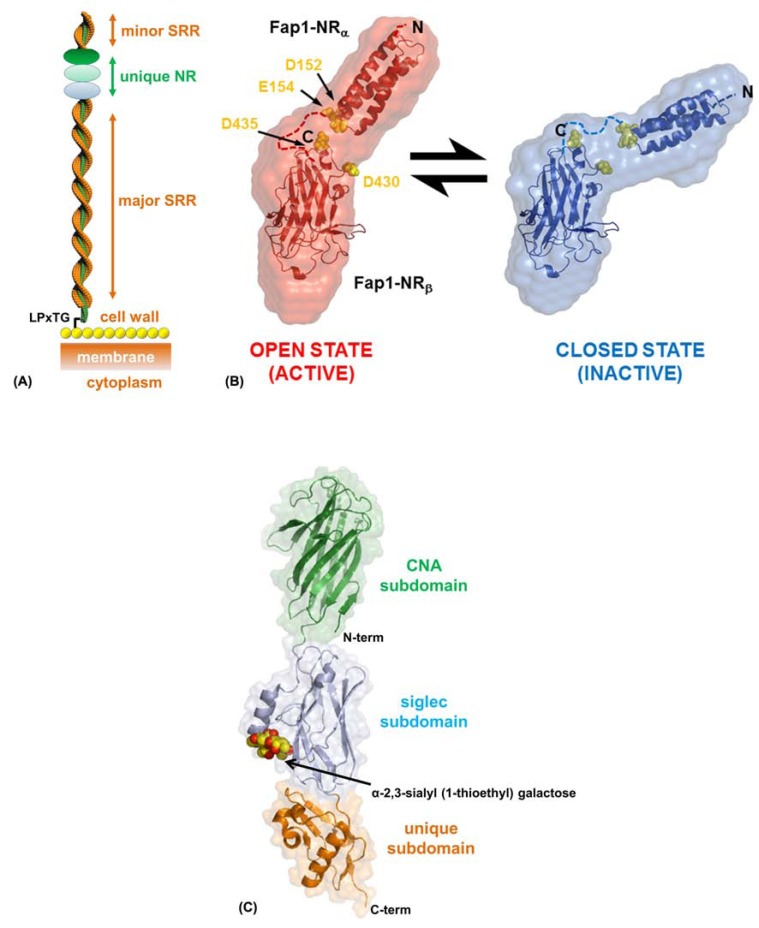
Fig. (3).
Adhesive mechanisms of SRRPs. (A) Schematic representation of a mature SRRP. The N-terminal unique adhesive region is projected away from the cell wall via the extensive SRR region. There is also a minor SRR at the N-terminal pole. The C-terminus is attached to the cell wall peptidoglycan (yellow spheres) through an LPxTG anchor sequence. (B) Conformations of the ‘open’ and ‘closed’ states of S. parasanguinis Fap1-NR. SAXS electron densities are shown as envelopes, coloured red (pH 5) or Blue (pH 8), and the structures have been docked into the maps. Acidic residues at the inter-subdomain boundary are highlighted as yellow spheres. (C) Crystal structure of the carbohydrate bound S. gordonii GspBBR.