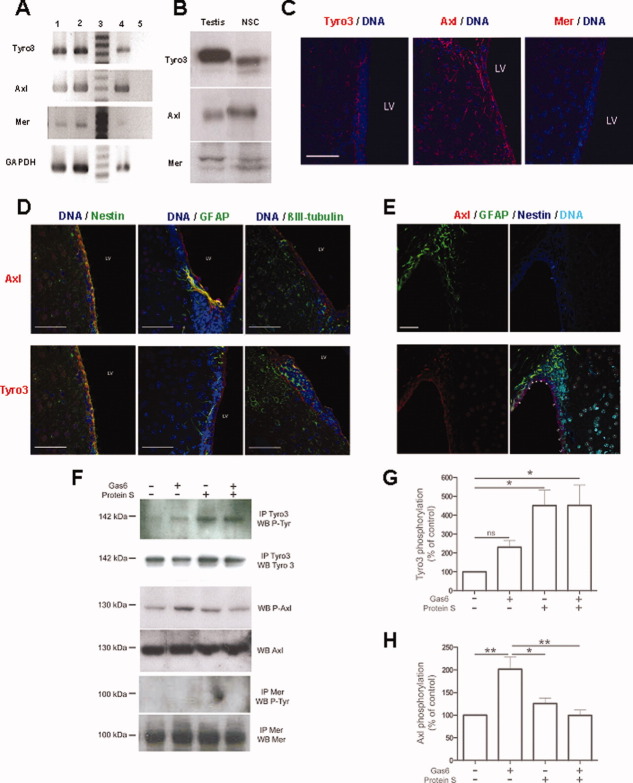
Figure 5.
Subventricular zone (SVZ) cells express Tyro3, Axl, and Mer (TAM) receptors that are activated by Gas6 or protein S. (A) Real time-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis of RNA obtained from two different (lanes 1 and 2) SVZ cell cultures using oligonucleotides reverse transcriptase specific for TAM or GAPDH used as a control. Lane 3 corresponds to DNA molecular weight markers. Lane 4 corresponds to RT-PCR products obtained using RNA from a tissue (testis) known to express TAM receptors (positive control) and lane 5 to RT-PCR performed in the absence of reverse transcription (negative control). (B) Western blotting analysis of 50–100 μg of protein of SVZ cell lysates (neural stem cell) using either anti-Tyro3, anti-Axl, or anti-Mer antibodies. Protein lysates (50–100 μg) from testis were used as positive control. (C): Immunostaining (red) of Axl, Tyro3, or Mer on SVZ mice brain sections. Scale bar = 60 μm. (D, E): Coimmunostaining of Axl (red) or Tyro3 (red) along with nestin or glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) or βIII tubulin (green, D) or GFAP (green, E) and nestin (blue, E). Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue D or cyan in E). Scale bar = 60 μm. (F–H): Western blotting analysis of cell lysates obtained from SVZ cell cultures maintained in serum-free medium (SFM) or in SFM supplemented with 10 μg ml−1 of Gas6, Protein S or both for 8 minutes. Cell lysates of 80 μg were either immunoprecipitated with anti-Tyro3 or anti-Mer antibody and immunoprecipitates analyzed by Western blotting (WB) with antiphosphotyrosine (P-Tyr), anti-Tyro3, and anti-Mer or were directly analyzed by Western blotting using either an anti-phospho-Axl antibody (P-Axl) or an anti-Axl antibody. The bands on the blots were quantified by densitometry and values were presented as means ± SEM. The statistical evaluation of the data was performed with ANOVA. * p < .05, ** p < .01. Abbreviations: GAPDH, glyceraldehade-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein.