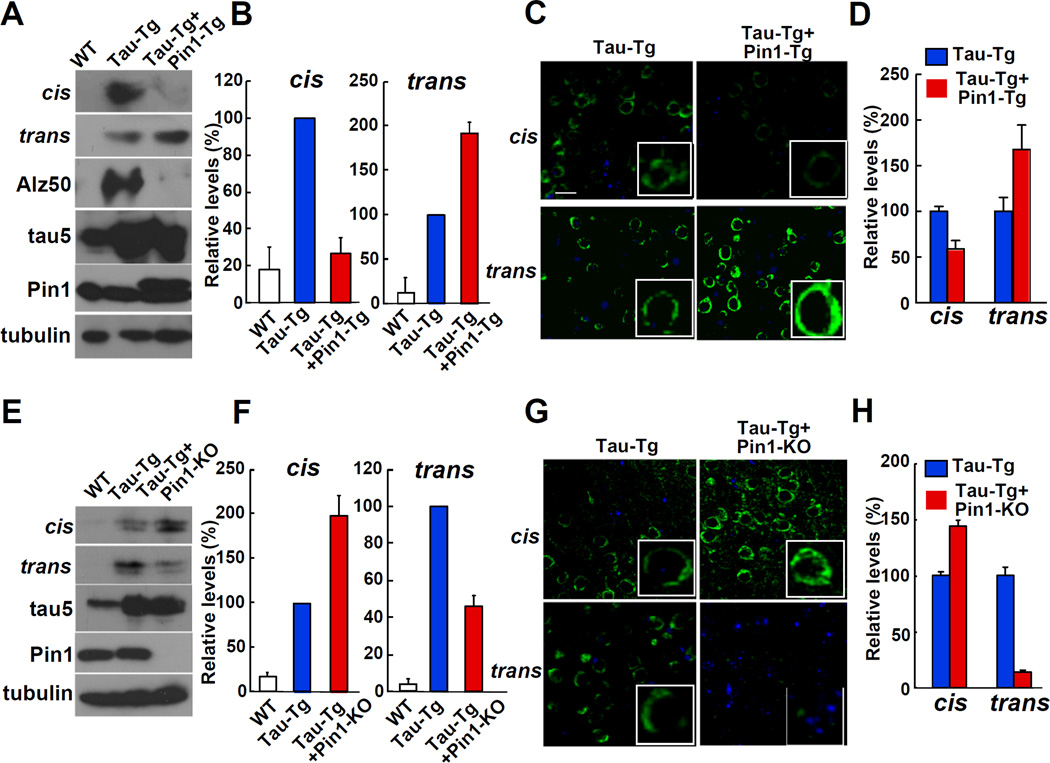
Figure 6. Whereas Pin1 Overexpression Increases the Cis to Trans Conversion of pT231-Tau, Pin1 Knockout Reduces the Conversion in AD Mouse Models.
(A-D) Pin1 overexpression decreases cis pThr231-Pro tau, but increases trans pT231-tau in tau transgenic mouse brains. Both immunoblotting (A, B) and immunostaining (C, D) analyses of the cerebral cortex of wild-type littermates (WT), tau transgenic (Tau-Tg), and tau and Pin1 double transgenic (Tau-Tg+Pin1-Tg) mice showed higher trans pThr231-Pro tau, but lower cis pT231-tau signals in Tau-Tg+Pin1-Tg than those in Tau-Tg mice.
(E-H), Pin1 knockout increases cis pThr231-Pro tau, but decreases trans pT231-tau in tau transgenic mouse brains. Both immunoblotting (E, F) and immunostaining (G, H) analyses of the cerebral cortex of mice revealed higher cis pThr231-Pro tau, but lower trans pT231-tau signals in Tau-Tg and Pin1 KO mice (Tau-Tg+Pin1-KO) than those in Tau-Tg mice. Scale bars, 20 µm.
See also Figure S6.