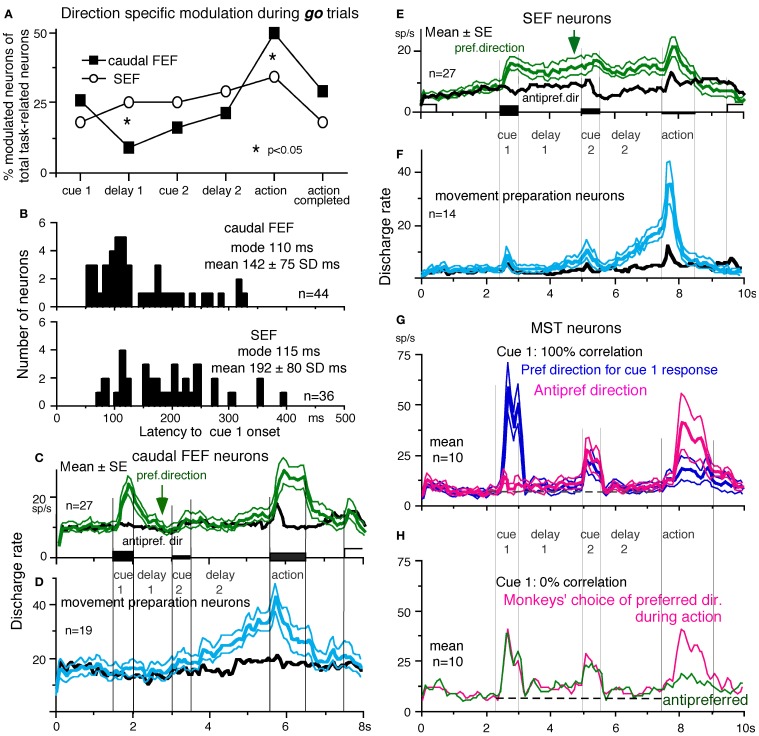
Figure 9.
Comparison of SEF and caudal FEF neuron discharge during memory-based pursuit. (A) Comparison of percent of modulated neurons in caudal FEF and SEF (of total task-related neurons) that exhibited direction-specific modulation during go trials. See legend of Figure 7 for the definition of task-related neurons. (B) Comparison of latencies of visual motion responses of caudal FEF and SEF neurons to cue 1. Neurons with shorter visual latencies were significantly more frequent in caudal FEF than SEF (p < 0.01). (C) Mean±SE discharge of 27 caudal FEF neurons that exhibited directional visual motion response to cue 1 during go trials. (E) Mean±SE discharge of 27 SEF neurons that exhibited directional visual motion response to cue 1 during go trials. In (C and E) Green and black traces are discharge modulation in the preferred direction and anti-preferred direction, respectively. (D and F) Mean±SE discharge of movement- preparation neurons in the caudal FEF (D) and SEF (F) during go trials. Blue and black traces are discharge modulation in the preferred direction and anti-preferred direction, respectively. (D and F) Reproduced from Shichinohe et al. (2009). (G and H) Reproduced from Kurkin et al. (2011). Others, reproduced from Fukushima et al. (2011a,b).