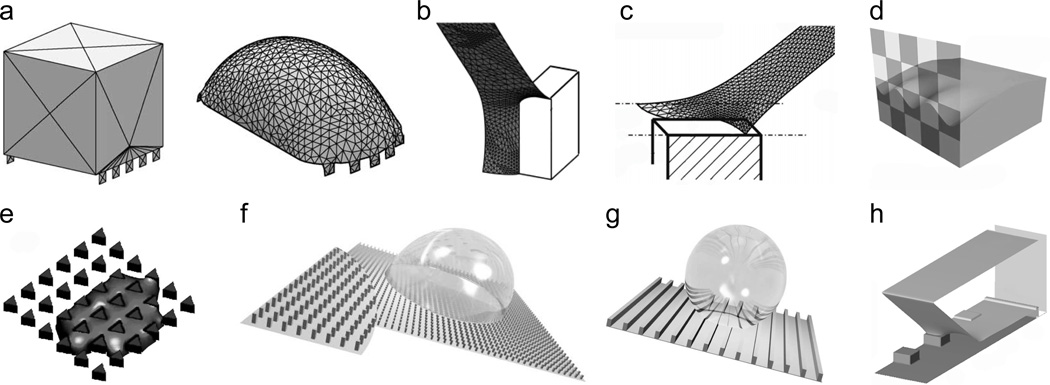
Figure 5.
Modeling wet adhesion on textured surfaces. (a) Initial and final Surface Evolver simulation profiles for a static drop on a pillared surface. Reprinted from Chen et al.,[94] copyright (2005), with permission from Elsevier. (b) Surface Evolver simulation of a portion of a droplet in a Wenzel state on a pillared surface. Reprinted with permission from Dorrer and Rühe.[97] Copyright (2008), American Chemical Society. (c) Surface Evolver simulation of a portion of a droplet in a Cassie state on a pillared surface. Reprinted with permission from Dorrer and Rühe.[95] Copyright (2007), American Chemical Society. (d) Surface Evolver simulation of a droplet advancing or receding on a checkerboard chemically patterned surface. Reprinted with permission from Kwon et al.[93] Copyright (2010), American Chemical Society. (e) Lattice Boltzmann simulation of directional spreading through an array of triangular pillars. Reprinted with permission of Blow et al.[106] Copyright 2009, Institute of Physics. (f,g) Lattice-Boltzmann simulations of drops sliding on pillared and grooved surfaces. Source: Hyväluoma et al.,[107] with kind permission of The European Physical Journal (EPJ). (h) Lattice Boltzmann simulation of a portion of a drop in a Cassie state receding on a pillared surface. Reprinted with permission from Mognetti and Yeomans.[111] Copyright (2010) American Chemical Society.