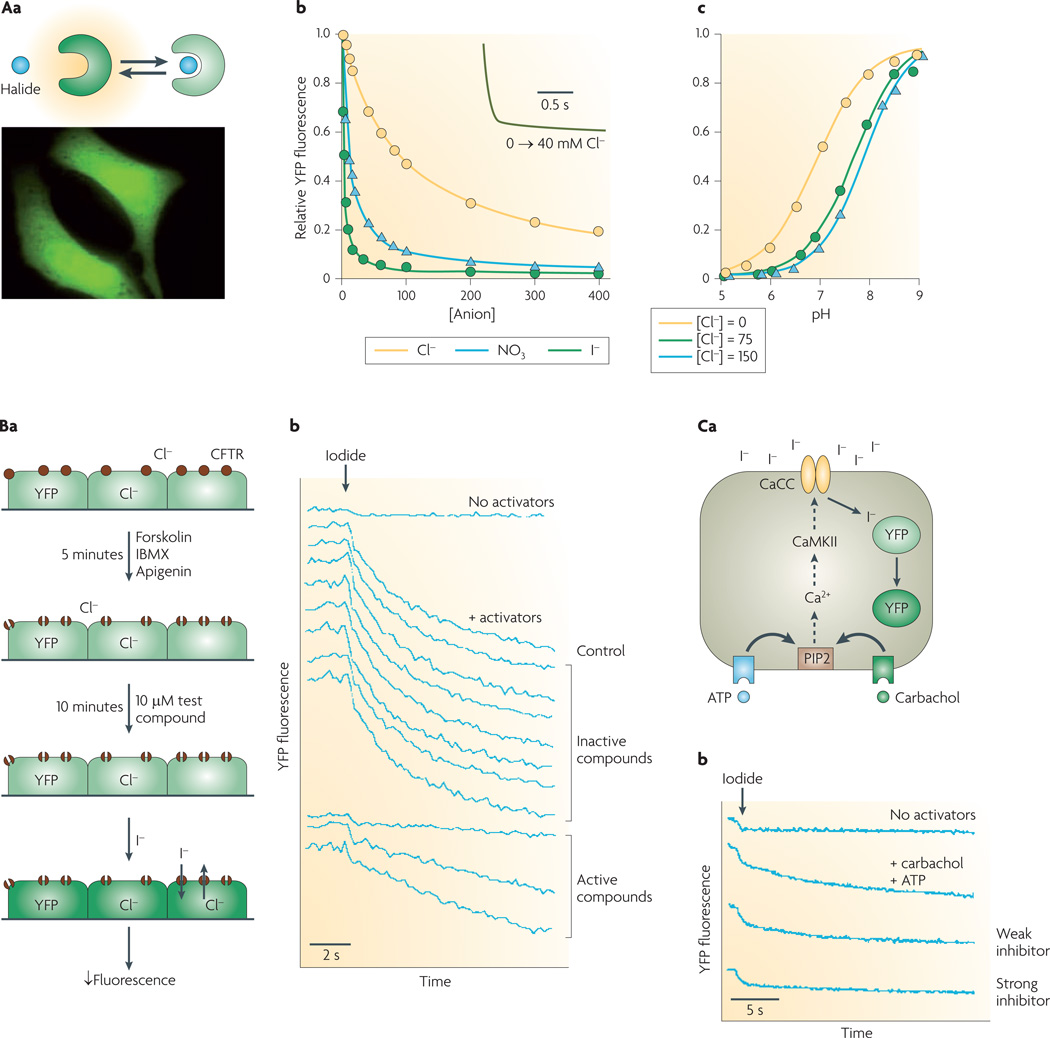
Figure 2. Cell-based screening assay of halide transport using a fluorescent protein mutant.
Aa | Reduced yellow fluorescence protein (YFP) fluorescence following halide binding (top). Cells expressing YFP in a cytoplasmic pattern (bottom). Ab | Titration of YFP-H148Q/I152L fluorescence with chloride, iodide and nitrate at pH 7.4. Inset shows rapid indicator response following an increase in Cl− concentration from 0 mM to 40 mM. Ac | pH titration at Cl− concentration of 0 mM, 75 mM and 150 mM. Ba | Screening protocol for cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (CFTR) inhibitors. CFTR halide conductance in cells co-expressing CFTR and YFP indicator stimulated by an agonist mixture (forskolin, 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX), apigenin). After addition of test compound, iodide influx is measured by YFP fluorescence. Bb | Single-well fluorescence data showing controls (no activators, no test compound) and test wells. Ca | Screen for calcium-activated chloride channel (CaCC) inhibitors. CaCC halide conduction in human colonic cells expressing native CaCC and transfected with YFP indicator is measured following stimulation by an agonist mixture (ATP, carbachol). Iodide influx quenches YFP fluorescence. Cb | Fluorescence data showing controls (no activators, no test compounds) and examples of inhibitors. CaMKII, calcium/calmodulin kinase II; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Panel A is modified, with permission, from REF. 5 © (2001) Elsevier Science. Panel B is modified, with permission, from REF. 6 © (2002) American Society for Clinical Investigation. Panel C is modified, with permission, from REF. 8 © (2008) American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.