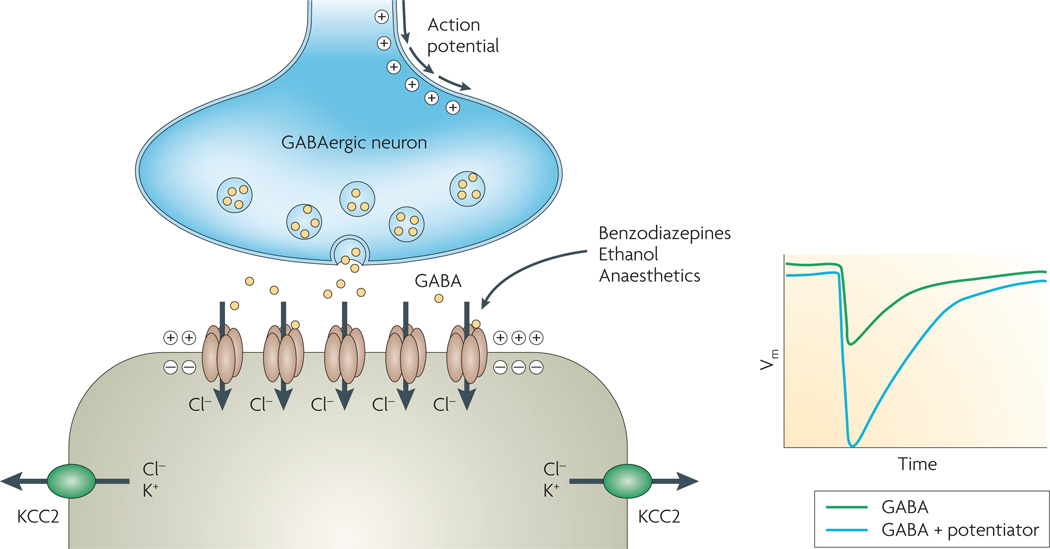
Figure 7. Ligand-gated chloride channels.
Schematic of GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) inhibitory synapse. Release of GABA from presynaptic membrane triggers the transient activation of ionotropic GABA receptors. The low intracellular chloride concentration in the postsynaptic neuron, generated by the action of the K+/Cl− cotransporter (KCC2), drives chloride influx through GABA-activated chloride channels causing membrane hyperpolarization. Benzodiazepines, anaesthetics, ethanol and other compounds act on GABA receptors to potentiate neurotransmitter effect. Vm, transmembrane potential.