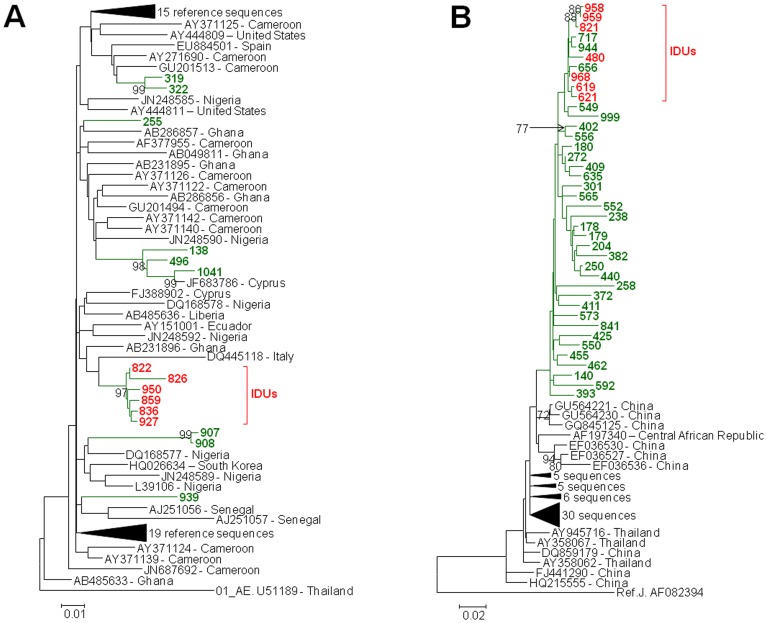
Figure 5. Inferred phylogenetic relationships of Bulgarian HIV-1 subtypes.
Tree structure was inferred using maximum likelihood analysis of polymerase sequences implemented in MEGA5. Support for each node was determined using 1,000 bootstrap replications with only values ≥70 shown. Scale bar indicates the number of nucleotide substitutions per site. Antiretroviral resistance-associated mutations were stripped from the alignments. Nearly identical tree topologies were also obtained with Bayesian analysis. (A) Subtype 02_AG. The 777-bp alignment was composed of 15 HIV-1 02_AG strains from Bulgaria and 71 02_AG reference sequences from the Los Alamos HIV database. The tree was rooted by using HIV-1 01_AE strain as the outgroup. Bulgarian sequences are shown using green branches and taxon names. Taxon names in red represent Bulgarian IDUs. (B) Circulating recombinant form (CRF) 01_AE. The 689-bp alignment was composed of 40 HIV-1 CRF 01_AE strains from Bulgaria and 60 subtype CRF 01_AE reference sequences from the Los Alamos HIV database. The tree was rooted by using HIV-1 subtype J as the outgroup. Bulgarian sequences are shown using green branches and taxon names. Taxon names in red represent Bulgarian IDUs.