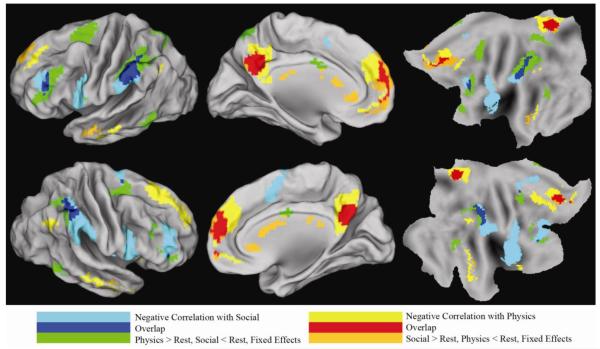
Figure 4.
Correspondence between antagonistic areas derived using task induced deviations from rest and anti-correlations networks derived from resting functional connectivity (without regressing whole brain signal). All areas corrected for multiple comparisons. Resting connectivity data from a separate group of subjects was used to derive regions anti-correlated with social antagonistic areas, and separately with mechanical antagonistic areas. The overlap of these anti-correlated areas with antagonistic areas is shown. Core brain areas involved in social reasoning tend to suppress core regions involved in mechanical reasoning, and vice-versa, even during unconstrained thought in the absence of a task.