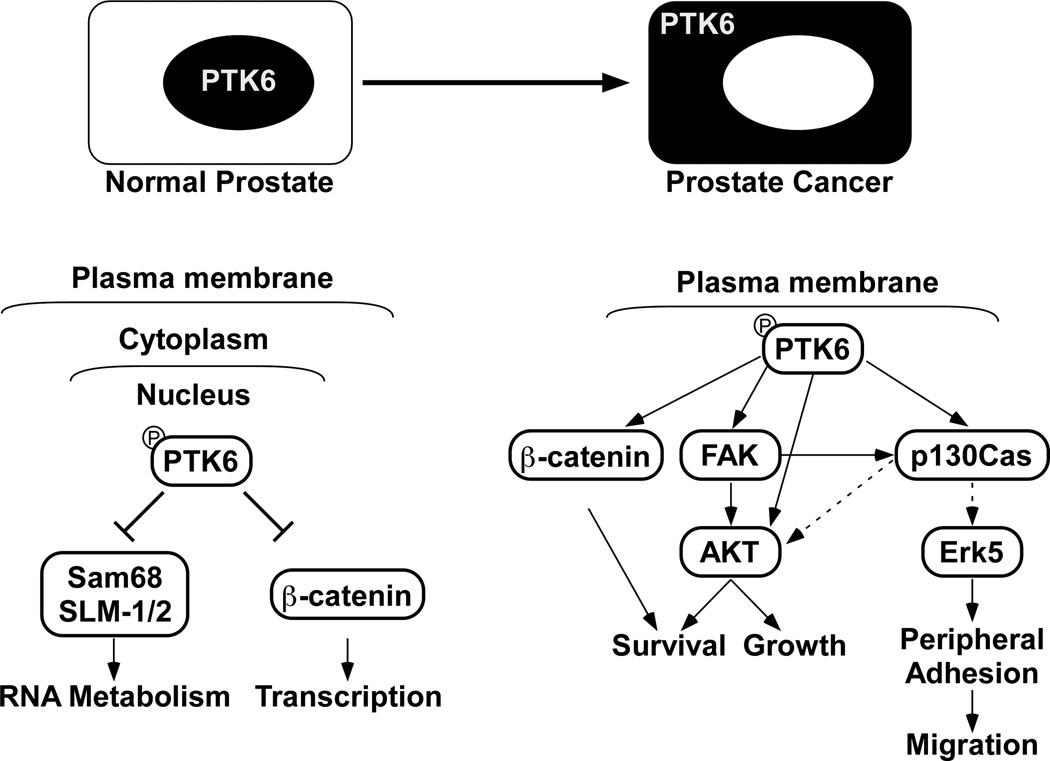
Fig. 1. Distinct functions for PTK6 in the nucleus and at the plasma membrane.
In normal prostate epithelial cells, total and active PTK6 is enriched in the nucleus where it has access to specific nuclear substrates and interacting proteins. These include the RNA binding proteins Sam68 [60] and SLM1 and SLM2 [48], as well as β-catenin [49]. PTK6 inhibits the RNA binding abilities of Sam68 [60] and the transcriptional activities of β-catenin [49]. Relocalization of PTK6 from nucleus to cytoplasm in prostate cancer facilitates its activation at the membrane. Active PTK6 can then phosphorylate and activate its cytoplasmic and membrane substrates including p130CAS [8], FAK [9], AKT [7], and β-catenin [49] to promote cancer cell proliferation, survival and migration.