Figure 4. Expression of Alix increases the accumulation of the C protein.
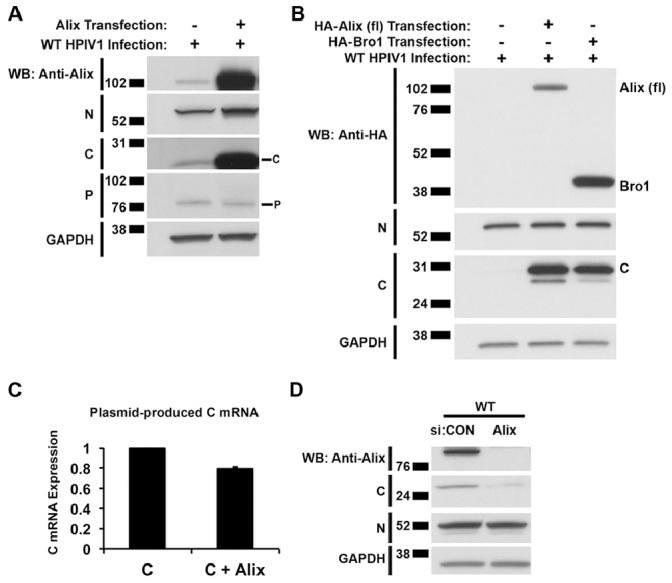
A. 293 T cells were mock-transfected or transfected with a plasmid expressing the Alix protein. 48 h later, the cells were infected with WT HPIV1, and, after another 24 h, cell lysates were prepared and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. Over-expression of Alix from a transfected plasmid during HPIV1 infection increased the accumulation of the C protein without affecting that of the N and P proteins. Full-length (fl) Alix over-expression in 293 T cells led to substantially increased C protein expression during WT HPIV1 infection. B. Using the same experimental protocol as in part A, the Bro1 domain was over-expressed, and it was sufficient to increase C protein expression during HPIV1 infection. C. The fl Alix and C expression constructs were co-transfected into 293 T cells, RNA was harvested at 48 h, and plasmid-produced C mRNA levels were measured by RT-qPCR. The increase in the abundance of plasmid-produced HPIV1 C proteins when Alix was over-expressed (Fig. 3B bottom panel) was not due to an increase in C mRNA levels. D. Knocking down endogenous Alix expression during HPIV1 infection reduced the accumulation of C protein with no effect on the N protein. Cells were transfected with control (CON) or Alix-specific siRNA as described in the Materials and Methods. The cells were then infected with WT HPIV1 and incubated for 24 h. Cell lysates were prepared and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using the indicated antibodies.
