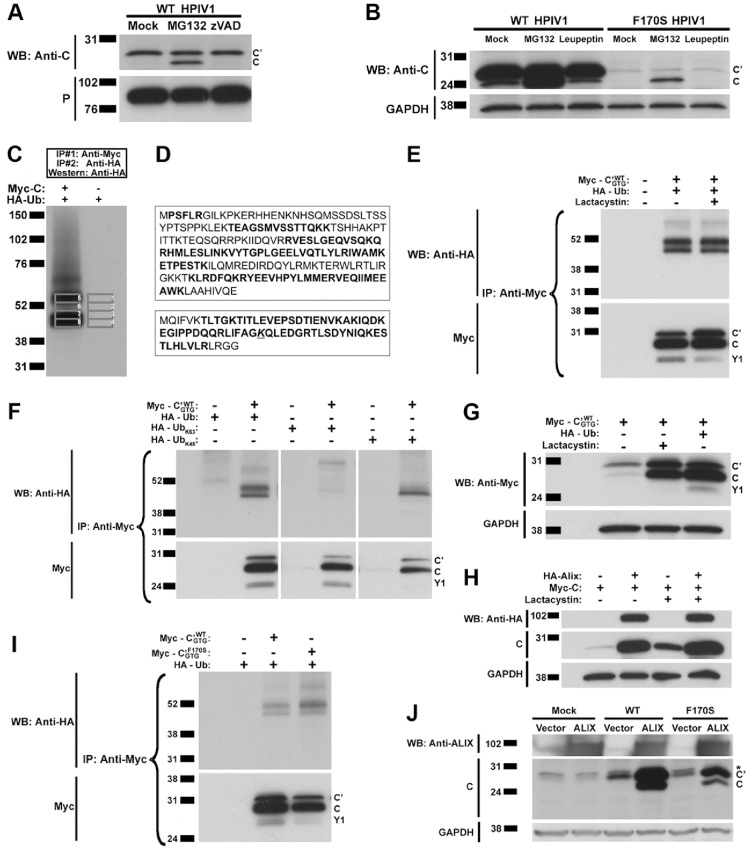
Figure 5. The C protein isoform is subject to proteasome-mediated degradation.
A and B. Analysis of the effect of various proteolytic inhibitors on C protein accumulation. A549 cells were infected with WT HPIV1 and then treated with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 (A and B), the pan-caspase inhibitor zVAD-FMK (A) or the lysosomal protease inhibitor leupeptin (B). Analysis of cell extracts by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting showed that only the proteasome inhibitor MG132 was associated with increased accumulation of the C isoform, whereas the C’ isoform was unaffected. C and D. Evidence for ubiquitination of the HPIV1 C protein. C. 293 T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing Myc-tagged C protein and HA-tagged ubiquitin (Ub). Two serial immunoprecipitations were performed, the first using anti-Myc antibodies to isolate the C protein, and the second using immobilized anti-HA antibodies to isolate ubiquitinated proteins. The proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting to visualize the ubiquitinated proteins. Bands 1–8 were excised from a duplicate gel that had been run in parallel and stained with Coomassie blue, and the gel slices were analyzed using mass spectrometry. Bands 1–4 served as a negative control. D. Amino acid sequences of the C protein (top) and ubiquitin (bottom) showing peptide sequences identified by mass spectrometry (bold). In addition, the Lys-48 residue of ubiquitin (underlined), but not Lys-63, was found to have evidence of a Gly-Gly modification corresponding to the presence of a poly-ubiquitin linkage. A Gly-Gly modification (underlined) corresponding to a poly-ubiquitin linkage was found at Lys-48 and not at Lys-63. E. Confirmation that the C protein is ubiquitinated. 293 T cells were transfected with Myc-tagged C’WT GTG and HA-tagged ubiquitin expression constructs and incubated in the presence or absence of the proteasome inhibitor lactacystin. The Myc-tagged C proteins were isolated by immunoprecipitation using anti-Myc antibodies, separated by SDS-PAGE, and then analyzed by Western blotting. F. Confirmation that the poly-ubiquitin linkage involves Lys-48. Plasmids expressing HA-tagged ubiquitin with every lysine mutated into an arginine except for Lys-63 (UbK63) or Lys-48 (UbK48) were transfected into 293 T cells together with plasmid expressing Myc-tagged C’WT GTG. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Myc antibodies to isolate the C protein and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting to detect the presence of poly-ubiquitin in the high molecular weight bands. G. The accumulation of C protein isoforms was increased by the over-expression of ubiquitin to a level comparable to that seen after treatment with a proteasome inhibitor. 293 T cells were transfected with HA-tagged ubiquitin and Myc-tagged C and subsequently treated with the proteasome inhibitor lactacystin. C protein expression was examined by Western blotting. H. The accumulation of C protein was also increased by the over-expression of Alix to a level comparable to that seen after treatment with a proteasome inhibitor. 293 T cells were transfected with HA-tagged Alix and Myc-tagged C and subsequently treated with the proteasome inhibitor lactacystin. C protein expression was examined by Western blotting as in part G. I. The F170S mutation-containing C proteins also undergo ubiquitination. 293 T cells were transfected with plasmid expressing HA-tagged ubiquitin with plasmids expressing Myc-tagged C’WT GTG or C’F170S GTG. As in panel F, cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Myc antibodies to isolate the C protein and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting to detect the presence of poly-ubiquitin in the high molecular weight bands. J. Alix over-expression increases the abundance of F170S mutation-containing C proteins but to a lesser extent compared to the WT C proteins. 293 T cells were transfected with plasmid expressing Alix and then infected with WT of F170S HPIV1. C protein expression was then examined by Western blotting. The * represents a non-specific band.