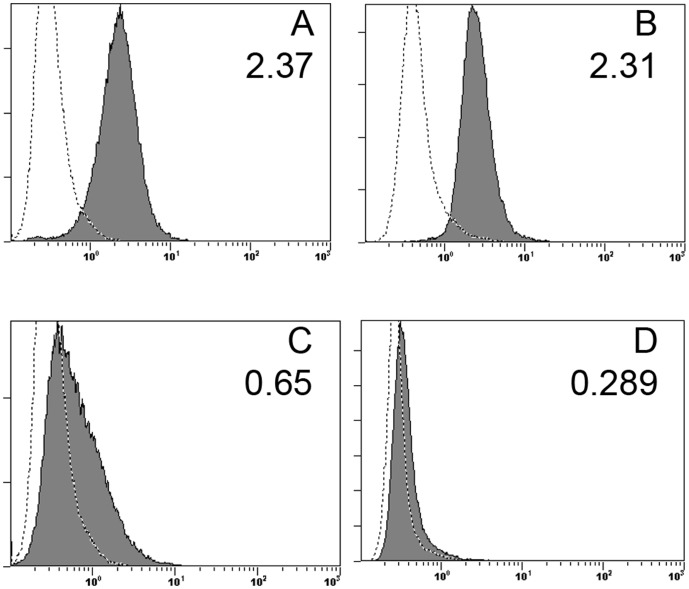
Figure 1. HLA I Antibody blocks binding of NKp44 fusion protein.
(A) DB cells express a ligand for NKp44 as seen through binding of 70 µg of NKp44-Ig (1 µg\ul), detected by anti-IgG-Fc-PE (filled histogram). As a negative control, DB cells were incubated with concentrated untransfected supernatant from HEK-293 cells (empty histogram). DB cells were first blocked with Human IgG Fc fragment to prevent reverse binding of fusion protein. (B) DB cells were incubated with mouse IgG2a isotype control (empty histogram) or 2.5 µg anti-HLA I, detected by anti-mIgG (H+L)-PE (filled) to measure expression of cell surface HLA I. (C) When incubating DB cells with 2.5 µg anti-HLA I antibody prior to incubation with 70 µg of NKp44 fusion protein and staining with anti-IgG-Fc-PE (filled histogram), fusion protein binding is reduced to near background levels as seen when staining DB cells with untransfected supernatant(empty histogram). Incubating cells with mouse IgG2a isotype did not block binding of NKp44 fusion protein (data not shown). (D) DB cells were incubated with 2.5 µg of anti-PCNA-Alexa-488 versus mIgG2a isotype control, demonstrating uniform expression of PCNA on the extracellular surface of DB cells. Mean Fluorescent Intensity is indicated in the top right corner of all plots.