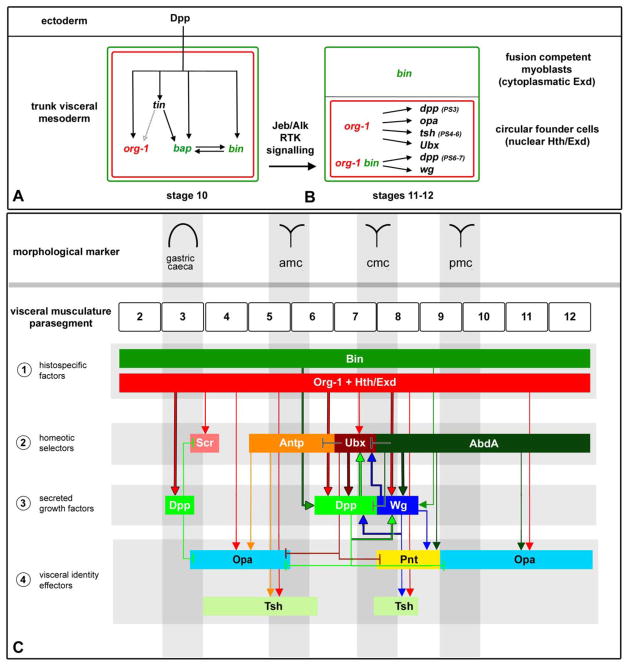
Figure 8. Regulatory interactions during trunk visceral mesoderm specification, founder cell diversification and midgut differentiation.
(A) At stage 10 all cells of the trunk visceral mesoderm primordia initiate the expression of tinman (tin), bagpipe (bap), binou (bin) and org-1 due to inductive decapentaplegic (dpp) cues from the ectoderm (only positive inputs are shown). (B) Whereas bap expression diminishes during stage 11, bin expression persists in all cells of the visceral mesoderm and org-1 expression is maintained under the influence of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling (RTK) from the Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (Alk) only in the founder cells of the visceral musculature. Alk signaling induces nuclear translocation of Homothorax/Extradenticle (Hth/Exd) that activate together with Org-1 in the visceral founder cells of PS3 dpp, of PS3-5 and PS9-12 opa, of PS4-6 tsh, and of PS7 Ubx, and together with Org-1 and Bin the founder cell specific expression of dpp in PS6-7 and of wg in PS8. This process results in the diversification of visceral muscle founder cell fates along the anteroposterior axis. (C) After muscle fusion the spatial expression patterns of opa, tsh, Ubx, dpp and wg in the founder cells expand to the respective muscle fibers. Additionally Org-1 initiates the expression of Sex combs reduced (Scr) in the visceral musculature and is required in addition to Wg for the activation of tsh expression in PS8. abd-A, wg and dpp initiate the expression domains of Pointed (pnt) in PS8-9. Demonstrated direct regulation is indicated by arrows outlined in black.