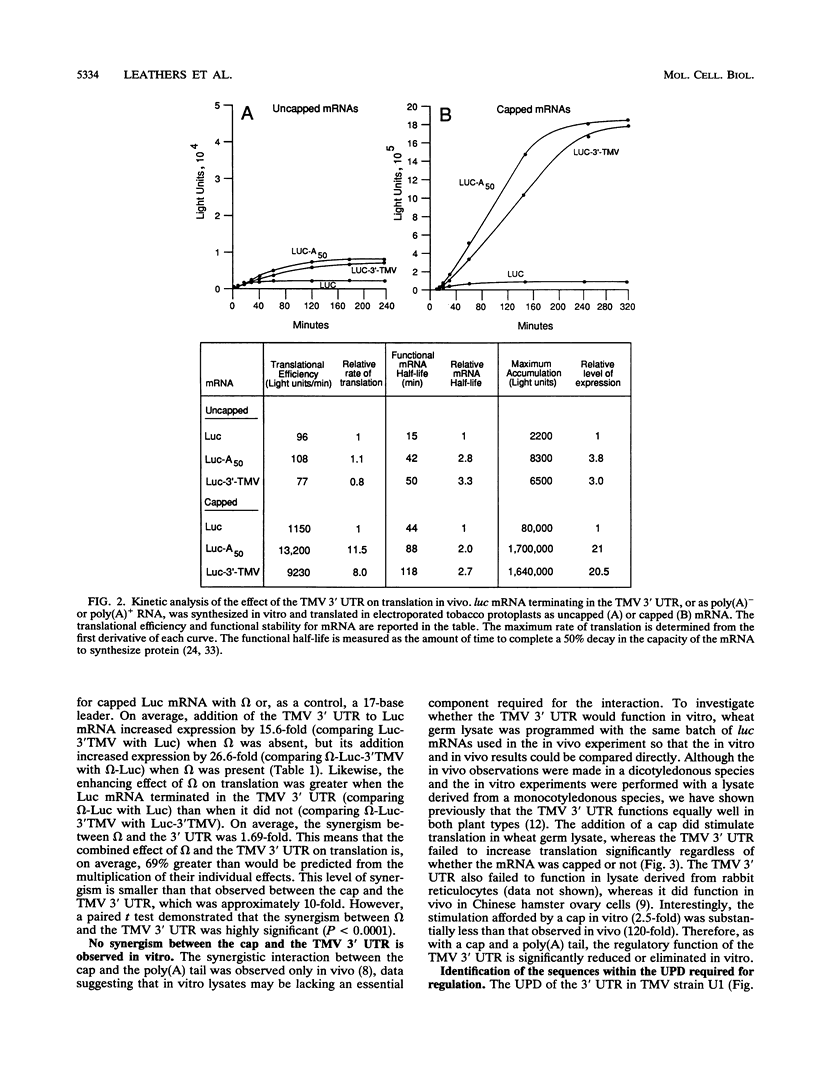
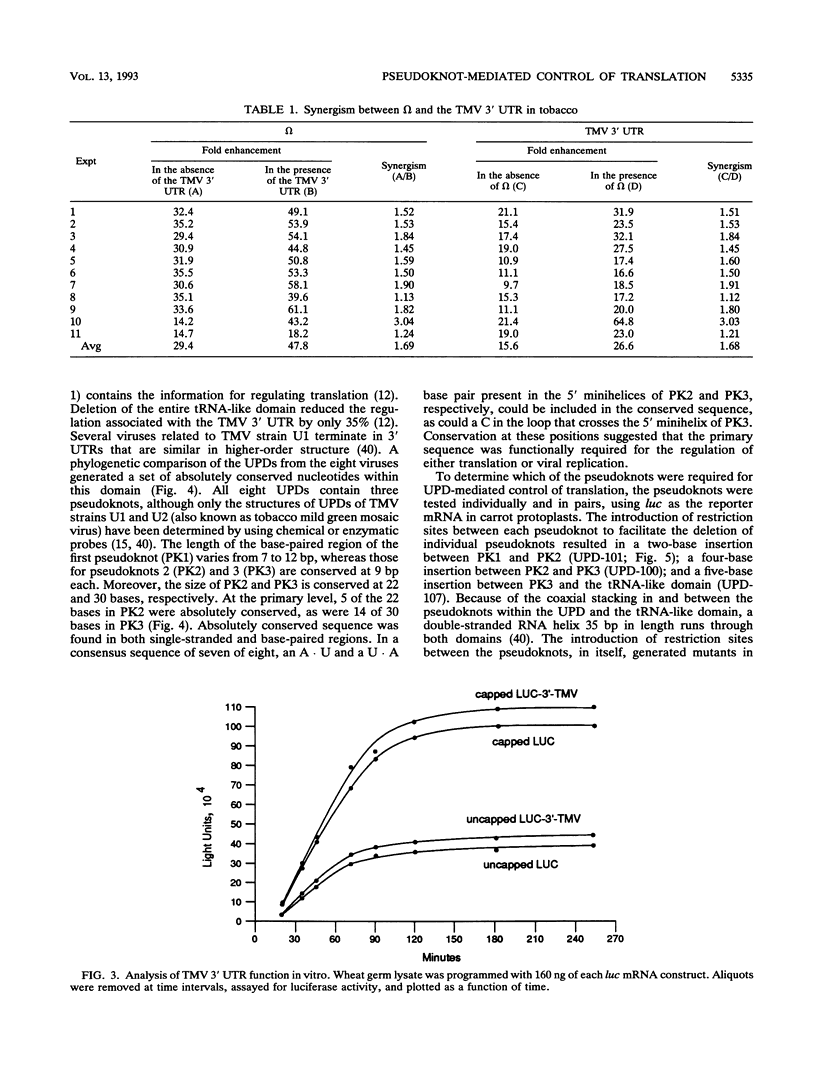
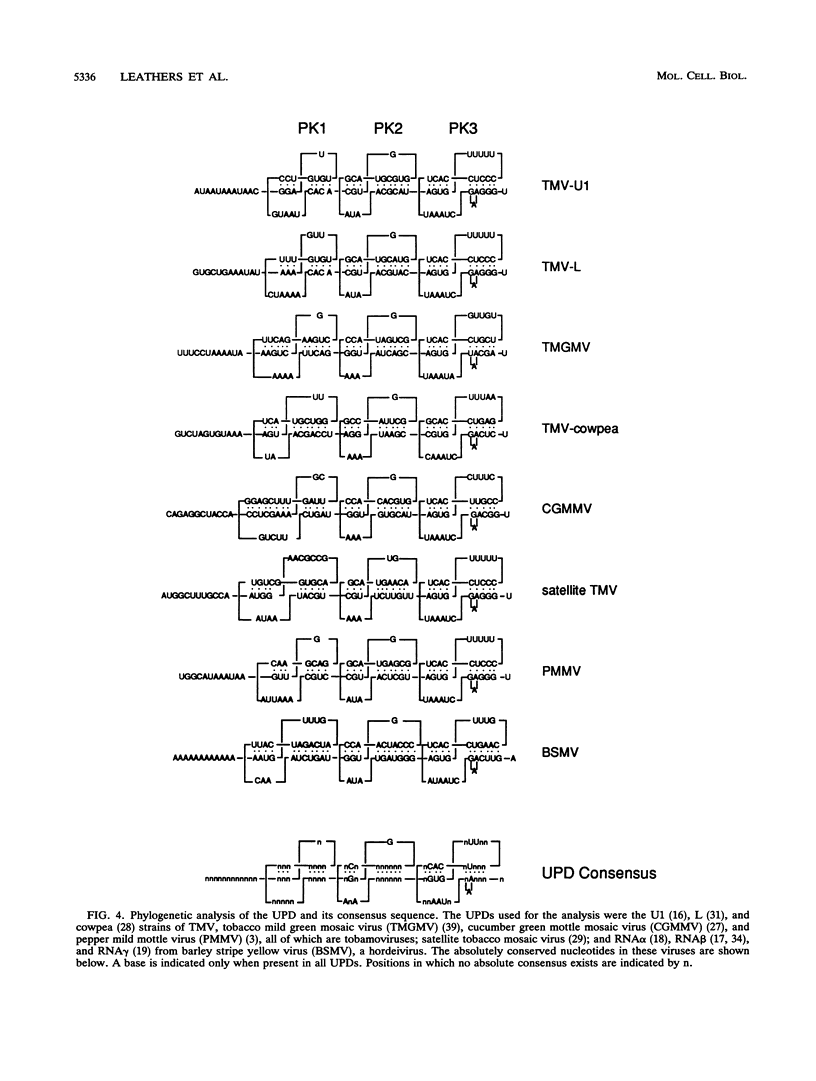
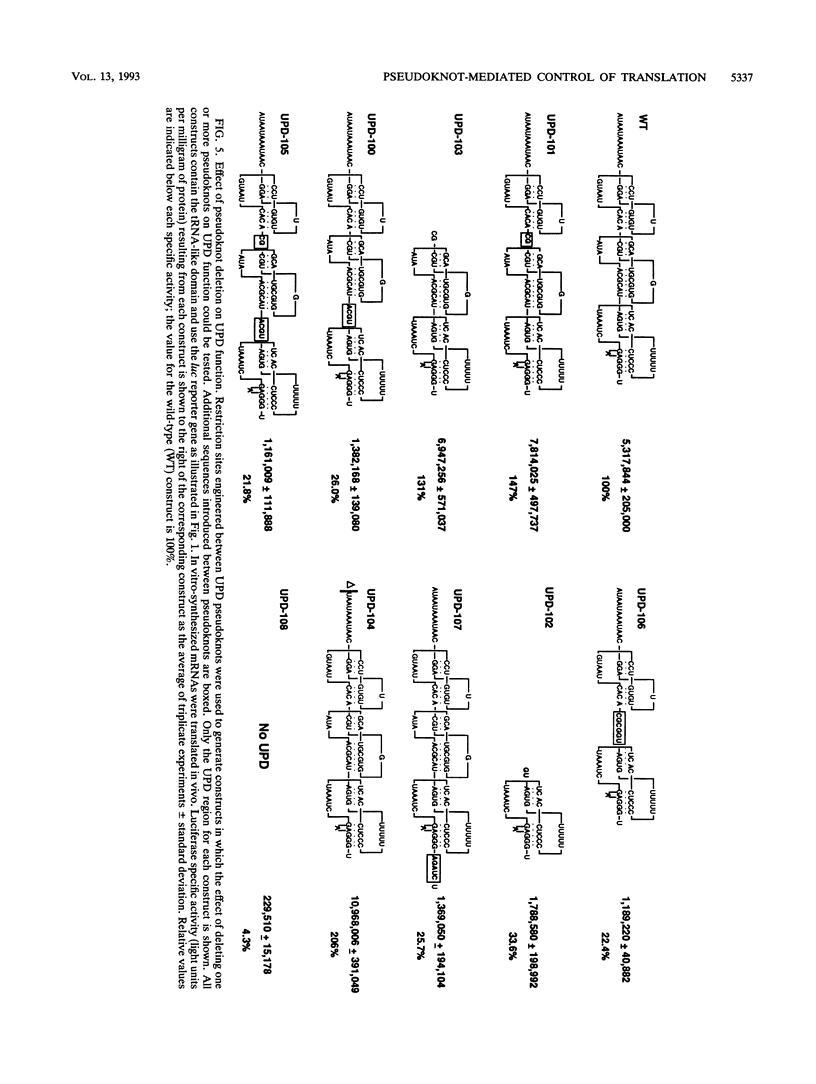
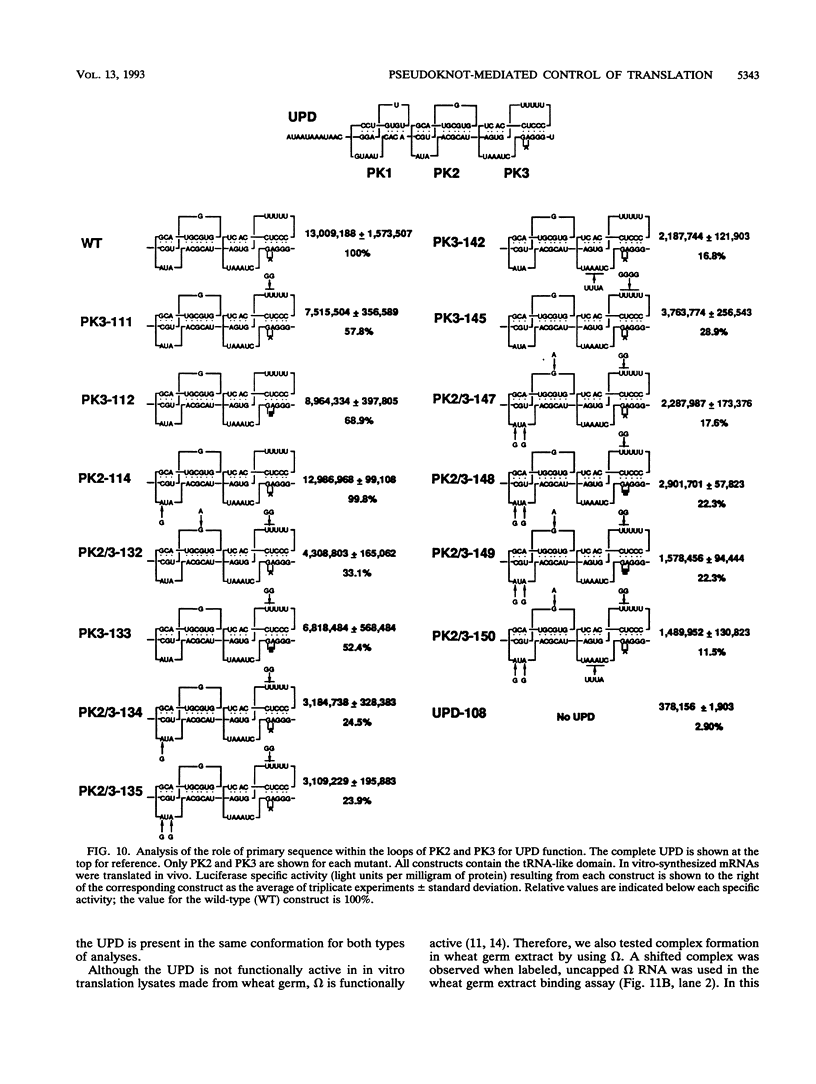
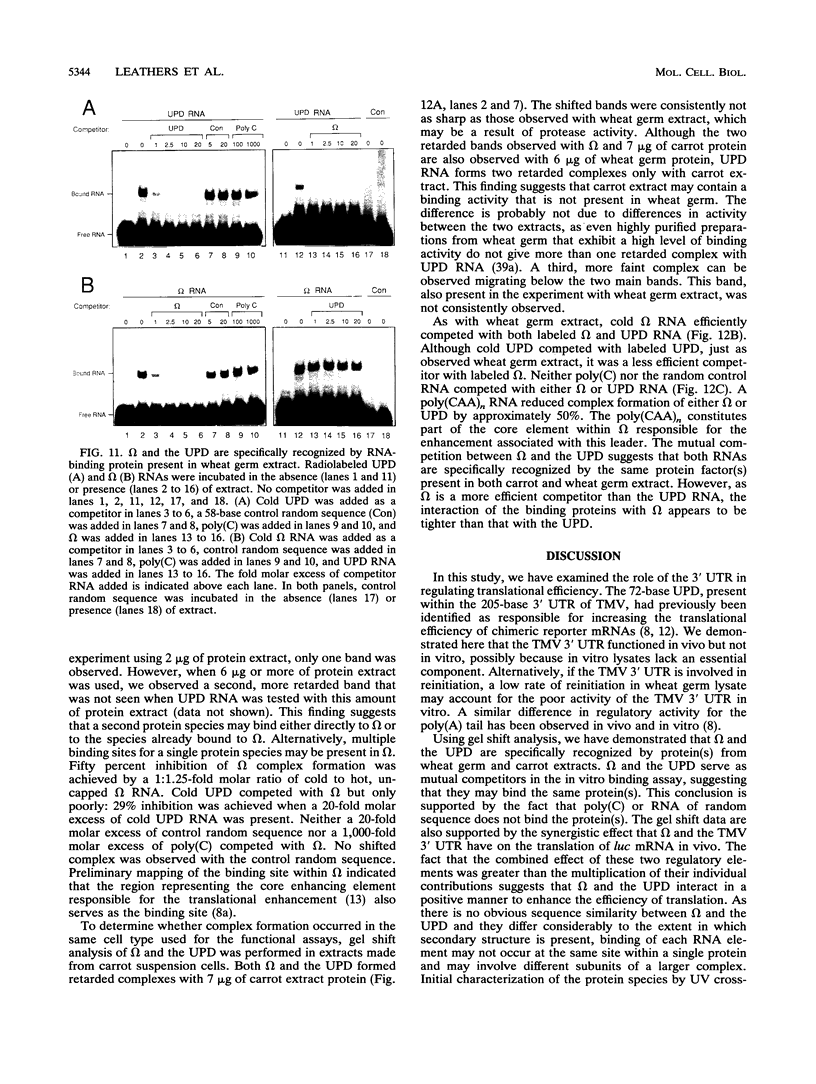
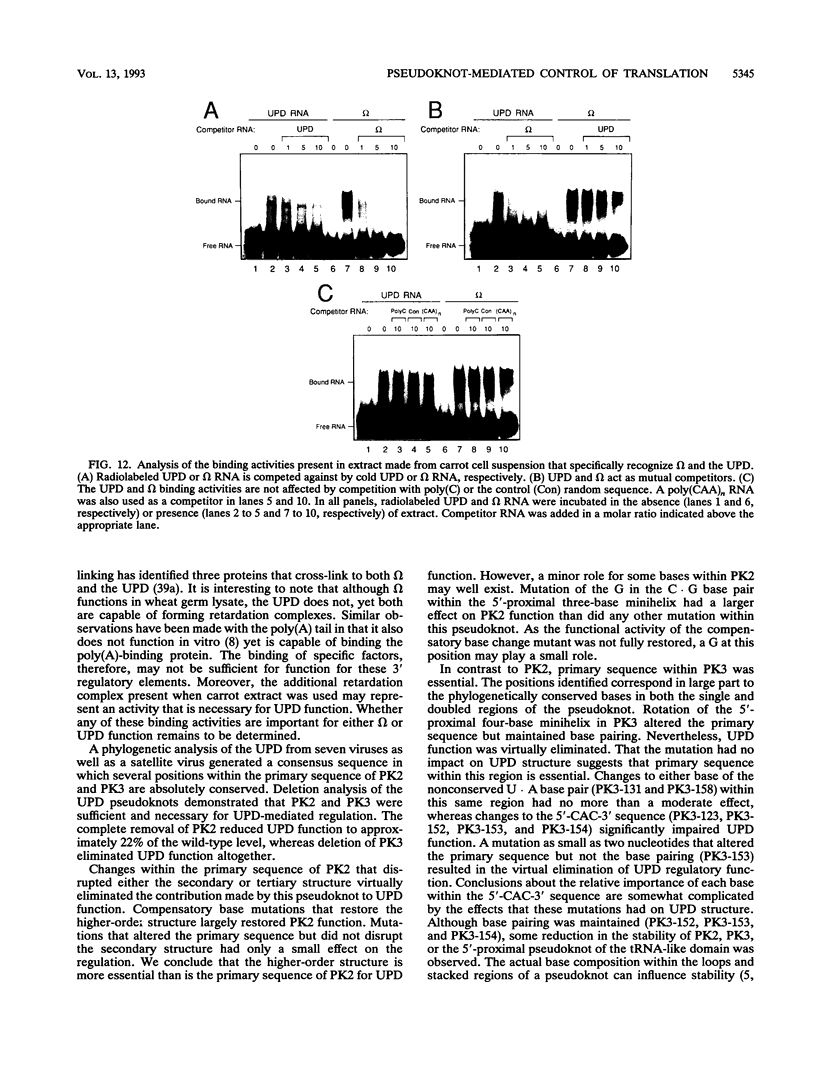
Abstract
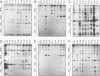
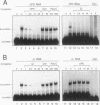
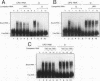
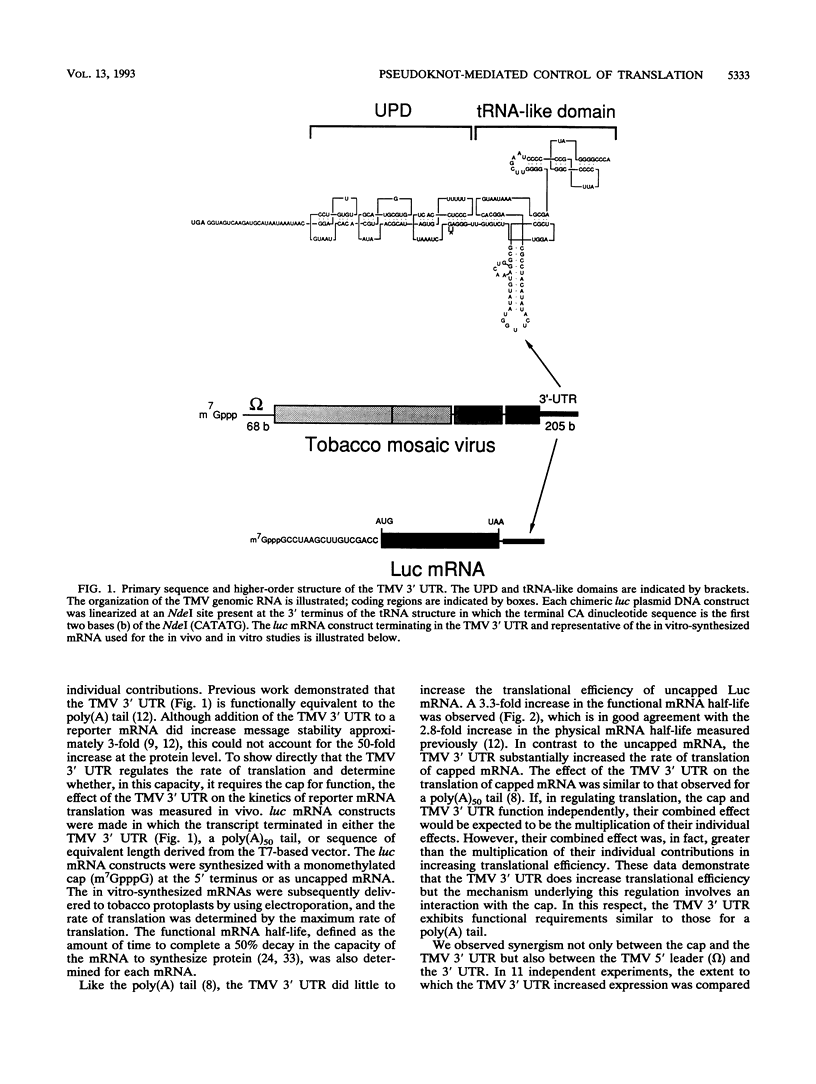
Both the 68-base 5' leader (omega) and the 205-base 3' untranslated region (UTR) of tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) promote efficient translation. A 35-base region within omega is necessary and sufficient for the regulation. Within the 3' UTR, a 52-base region, composed of two RNA pseudoknots, is required for regulation. These pseudoknots are phylogenetically conserved among seven viruses from two different viral groups and one satellite virus. The pseudoknots contained significant conservation at the secondary and tertiary levels and at several positions at the primary sequence level. Mutational analysis of the sequences determined that the primary sequence in several conserved positions, particularly within the third pseudoknot, was essential for function. The higher-order structure of the pseudoknots was also required. Both the leader and the pseudoknot region were specifically recognized by, and competed for, the same proteins in extracts made from carrot cell suspension cells and wheat germ. Binding of the proteins is much stronger to omega than the pseudoknot region. Synergism was observed between the TMV 3' UTR and the cap and to a lesser extent between omega and the 3' UTR. The functional synergism and the protein binding data suggest that the cap, TMV 5' leader, and 3' UTR interact to establish an efficient level of translation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angenent G. C., Linthorst H. J., van Belkum A. F., Cornelissen B. J., Bol J. F. RNA 2 of tobacco rattle virus strain TCM encodes an unexpected gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4673–4682. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwater J. A., Wisdom R., Verma I. M. Regulated mRNA stability. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:519–541. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avila-Rincon M. J., Ferrero M. L., Alonso E., García-Luque I., Díaz-Ruíz J. R. Nucleotide sequences of 5' and 3' non-coding regions of pepper mild mottle virus strain S RNA. J Gen Virol. 1989 Nov;70(Pt 11):3025–3031. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-11-3025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheong C., Varani G., Tinoco I., Jr Solution structure of an unusually stable RNA hairpin, 5'GGAC(UUCG)GUCC. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):680–682. doi: 10.1038/346680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelissen B. J., Linthorst H. J., Brederode F. T., Bol J. F. Analysis of the genome structure of tobacco rattle virus strain PSG. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2157–2169. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallie D. R., Feder J. N., Schimke R. T., Walbot V. Post-transcriptional regulation in higher eukaryotes: the role of the reporter gene in controlling expression. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Aug;228(1-2):258–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00282474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallie D. R., Lucas W. J., Walbot V. Visualizing mRNA expression in plant protoplasts: factors influencing efficient mRNA uptake and translation. Plant Cell. 1989 Mar;1(3):301–311. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.3.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallie D. R., Sleat D. E., Watts J. W., Turner P. C., Wilson T. M. The 5'-leader sequence of tobacco mosaic virus RNA enhances the expression of foreign gene transcripts in vitro and in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3257–3273. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallie D. R. The cap and poly(A) tail function synergistically to regulate mRNA translational efficiency. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):2108–2116. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.2108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallie D. R., Walbot V., Hershey J. W. The ribosomal fraction mediates the translational enhancement associated with the 5'-leader of tobacco mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8675–8694. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallie D. R., Walbot V. Identification of the motifs within the tobacco mosaic virus 5'-leader responsible for enhancing translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 11;20(17):4631–4638. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.17.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallie D. R., Walbot V. RNA pseudoknot domain of tobacco mosaic virus can functionally substitute for a poly(A) tail in plant and animal cells. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1149–1157. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Arenal F. Sequence and structure at the genome 3' end of the U2-strain of tobacco mosaic virus, a histidine-accepting tobamovirus. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goelet P., Lomonossoff G. P., Butler P. J., Akam M. E., Gait M. J., Karn J. Nucleotide sequence of tobacco mosaic virus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5818–5822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson G., Armour S. L., Gamboa G. C., Burgett S. G., Shepherd J. W. Nucleotide sequence of barley stripe mosaic virus RNA alpha: RNA alpha encodes a single polypeptide with homology to corresponding proteins from other viruses. Virology. 1989 Jun;170(2):370–377. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson G., Armour S. L. The complete nucleotide sequence of RNA beta from the type strain of barley stripe mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3895–3909. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson G., Hunter B., Hanau R., Armour S. L., Jackson A. O. Nucleotide sequence and genetic organization of barley stripe mosaic virus RNA gamma. Virology. 1987 Jun;158(2):394–406. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90211-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haenni A. L., Joshi S., Chapeville F. tRNA-like structures in the genomes of RNA viruses. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1982;27:85–104. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60598-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall T. C. Transfer RNA-like structures in viral genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1979;60:1–26. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61257-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. E., Böhni R., Schneiderman M. H., Ramamurthy L., Schümperli D., Marzluff W. F. Regulation of histone mRNA in the unperturbed cell cycle: evidence suggesting control at two posttranscriptional steps. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2416–2424. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. The organization and expression of histone gene families. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEPES A. KINETICS OF INDUCED ENZYME SYNTHESIS. DETERMINATION OF THE MEAN LIFE OF GALACTOSIDASE-SPECIFIC MESSENGER RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Oct 15;76:293–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meshi T., Ohno T., Iba H., Okada Y. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned cDNA copy of TMV (cowpea strain) RNA, including the assembly origin, the coat protein cistron, and the 3' non-coding region. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):20–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00271189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkov T. E., Mathews D. M., Du Plessis D. H., Dodds J. A. Nucleotide sequence and translation of satellite tobacco mosaic virus RNA. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):139–146. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90361-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munroe D., Jacobson A. Tales of poly(A): a review. Gene. 1990 Jul 16;91(2):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno T., Aoyagi M., Yamanashi Y., Saito H., Ikawa S., Meshi T., Okada Y. Nucleotide sequence of the tobacco mosaic virus (tomato strain) genome and comparison with the common strain genome. J Biochem. 1984 Dec;96(6):1915–1923. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey N. B., Marzluff W. F. The stem-loop structure at the 3' end of histone mRNA is necessary and sufficient for regulation of histone mRNA stability. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4557–4559. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S., Reeh S. Functional mRNA half lives in E. coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Nov 9;166(3):329–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00267626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi J. D., Wyatt J. R., Tinoco I., Jr Conformation of an RNA pseudoknot. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 20;214(2):437–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90192-O. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Davis R. W., Kornberg R. D. A single domain of yeast poly(A)-binding protein is necessary and sufficient for RNA binding and cell viability. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3268–3276. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Davis R. W. The poly(A) binding protein is required for poly(A) shortening and 60S ribosomal subunit-dependent translation initiation. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):857–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90938-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Davis R. W. Translation initiation and ribosomal biogenesis: involvement of a putative rRNA helicase and RPL46. Science. 1990 Mar 2;247(4946):1077–1079. doi: 10.1126/science.2408148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solis I., Garcia-Arenal F. The complete nucleotide sequence of the genomic RNA of the tobamovirus tobacco mild green mosaic virus. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):553–558. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90520-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Castle E. Analysis of structural properties which possibly are characteristic for the 3'-terminal sequence of the genome RNA of flaviviruses. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jun;67(Pt 6):1183–1188. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-6-1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yisraeli J. K., Melton D. A. Synthesis of long, capped transcripts in vitro by SP6 and T7 RNA polymerases. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:42–50. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Belkum A., Abrahams J. P., Pleij C. W., Bosch L. Five pseudoknots are present at the 204 nucleotides long 3' noncoding region of tobacco mosaic virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7673–7686. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]