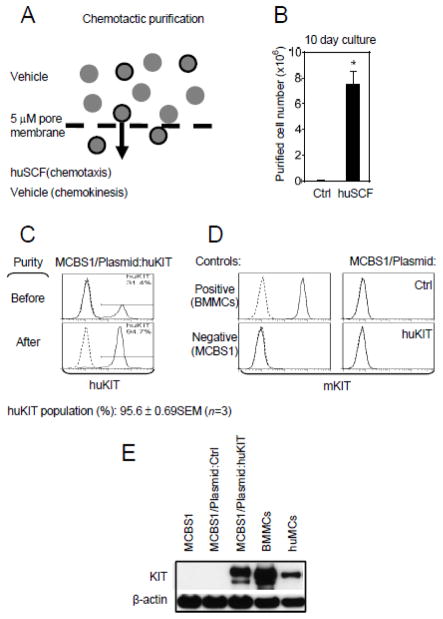
Fig. 4.
Chemotactic purification of huKIT-transduced MCBS1 MCs. (A) Schematic diagram. (B) Purified huKIT-transfectants, derived as shown in A, were cultured for 10 days and the number of cells recovered was determined. The cells subjected to chemotactic purification driven towards vehicle alone (chemokinesis) were used as a negative control (Ctrl). (C) The content of huKIT-expressing populations of the purified transfectants in A was evaluated by flow cytometry. (D) Surface expression of mKIT in non-transduced MCBS1 MCs (MCBS1), empty plasmid transfected (MCBS1/Plasmid:Ctrl), or chemotactically purified huKIT-transduced cells from A (MCBS1/Plasmid:huKIT) was determined by flow cytometry. Four to six week old cultured regular non-dividing mouse BMMCs were used as a positive control. (E) Immunoblot analysis for the presence of KIT (both mouse and human) in cells analyzed in D. Four to six week old cultured regular non-dividing mouse BMMCs were used as a positive control. In C-E, data of representative experiments performed from 3 independent sample preparations, transfections, or cells from 3 mice (regular non-dividing BMMCs) or donors (huMC) are shown. In B, data represents means and SEM (n=3 huKIT transfectants purified chemotactically) and a difference between the huSCF- and vehicle-driven purifications is indicated (*; P<0.05, Student’s t-test).