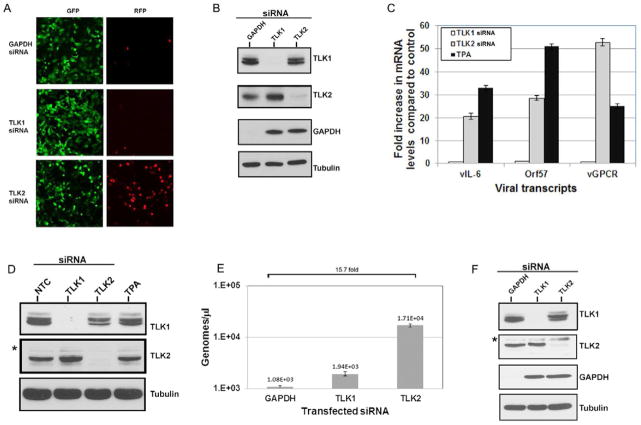
Figure 2. TLK2 Plays a Role in KSHV Reactivation.
A) Knockdown of TLK2 reactivates KSHV. KSHV-293 cells were reverse transfected with a final siRNA concentration of 25nM. A single GAPDH siRNA or a pool of 4 siRNAs against TLK1 or TLK2 were used. At 70 hours post-transfection, images were taken on a fluorescent microscope. B) siRNAs efficiently knock down target. Cellular lysates from the samples imaged in Fig. 2A were harvested and Western blots were performed for TLK1, TLK2, GAPDH, and the loading control tubulin. C) Viral lytic mRNAs are expressed. KSHV-293 cells were either mock transfected or reverse transfected with 50nM of the non-targeting control siRNA or the pooled TLK1 or TLK2 siRNAs. The mock transfected sample was treated with 25 ng/mL of TPA at the time of transfection. Levels of viral lytic transcripts, vIL-6, Orf57, and vGPCR, were measured by qPCR at 54 hours post-transfection. Values are normalized to the control siRNA. D) Western blots were performed for the indicated proteins for the experiment described in 2C. E) KSHV-293 cells were reverse transfected as described above in 2C. At 96 hours post-transfection, DNA was harvested and viral load was determined by qPCR. Primers for Orf57 were used as the indicator of viral genome copies. F) Western blots were performed for the indicated proteins to confirm knockdown in the experiment described in 2E. Non-specific bands are indicated by an asterisk “*”. Error bars represent standard deviation from the mean. Data were analyzed using a two-tailed type II Student’s t test for significance. See also Fig. S2.