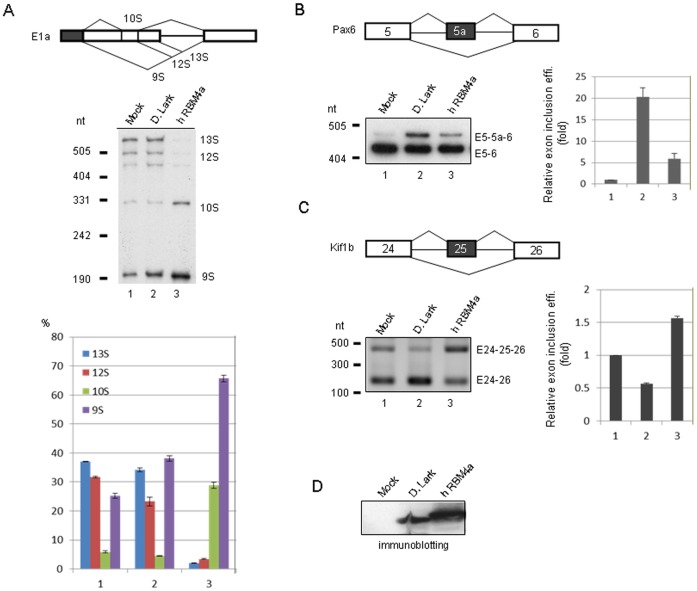
Figure 3. Drosophila Lark acts as a splicing regulatory protein.
The expression vector of FLAG-tagged human RBM4a or Drosophila Lark was cotransfected with a splicing minigene reporter, adenovirus E1a (A), Pax6 (B) or Kif1b (C), into HeLa (A) or HEK293 (B and C) cells; the minigenes are shown in each panel. Mock represents the empty expression vector. To detect the splicing products, RT-PCR was performed using total RNA as template, and then the resulting products were separated on polyacrylamide gels (E1a and Pax6) or agarose gels (Kif1b). Except for Kif1b, RT-PCR products were further blotted onto membranes, and detected by hybridization with 32P-labeled specific probe (Table 1). For E1a, the bar graph shows the relative abundance (%) of the major splicing products. For Pax6 and Kif1b, relative exon inclusion efficiencies are indicated below the gel or blot. Exon inclusion efficiency was calculated as exon-included RNA/total RNA. Bar graph shows exon inclusion fold relative to the mock; bar graph shows average values with standard deviations obtained from three independent experiments. (D) Immunoblotting using anti-FLAG shows overexpressed FLAG-tagged Lark and RBM4a.