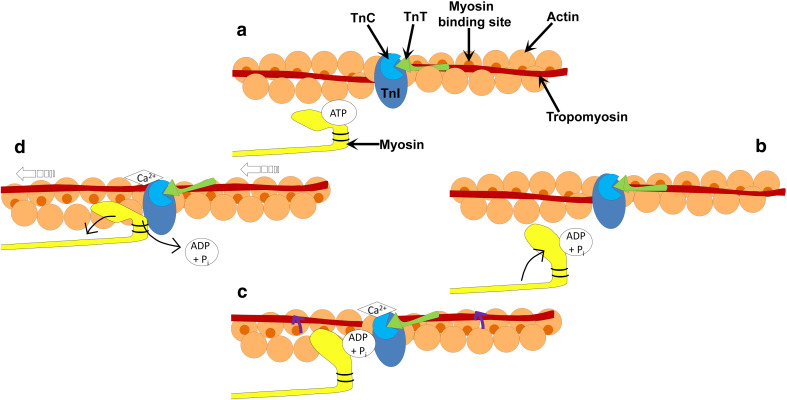
Fig. 4.
Schematic diagram of the cross-bridge cycle. a ATP binds to the ATP-binding domain on the myosin head. b ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP and a phosphate allowing the myosin head to move towards the actin filament. c Binding of Ca2+ to troponin C (TnC) results in a conformational change in the troponin complex, allowing the movement of tropomyosin around the actin filament (as indicated by the purple arrows). d Release of the hydrolyzed nucleotides results in the extension of the myosin head permitting the sliding of the filaments (open arrows). ATP quickly rebinds to the ATP-binding site on the myosin head, allowing dissociation of the myosin away from the actin filament, and the cycle is repeated