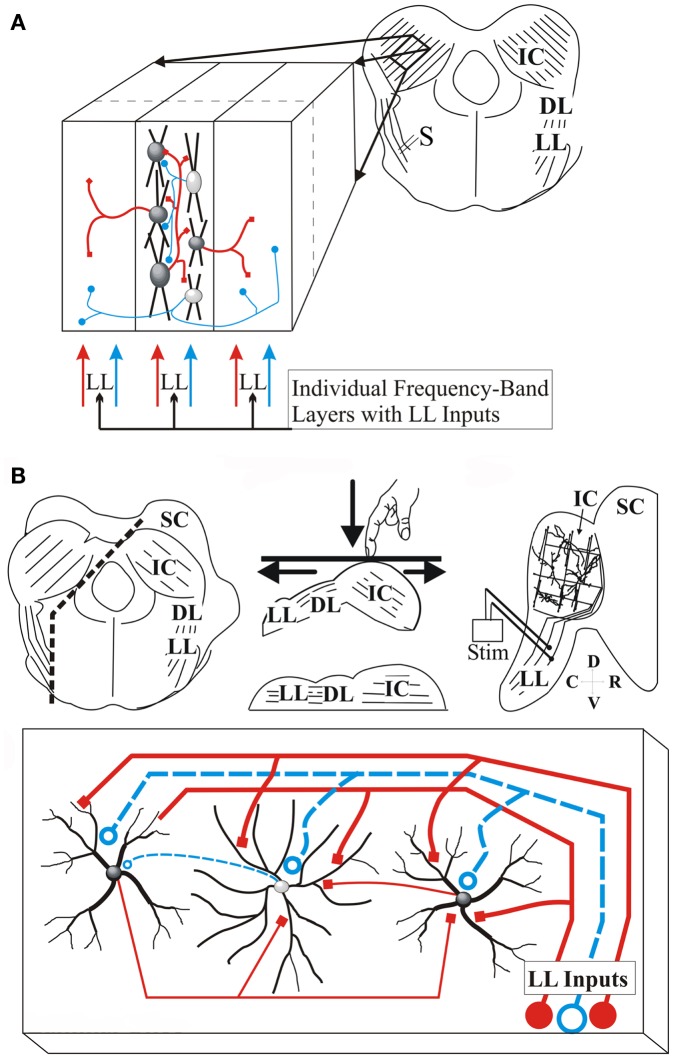
Figure 1.
Transverse and laminar slice planes of the IC. (A) Schematic of the transverse IC slice. Right, slice plane with parallel arrangement of laminae; IC, inferior colliculus; LL, lateral lemniscus; DL, dorsal nucleus of the lateral lemniscus; S, Lemniscal stimulating electrode; Left, Expanded region of the slice illustrates laminar and cross-laminar arrangement with lemniscal input; Center section, arrangement of cells within a lamina with intra-laminar connections; Left and right sections, neighboring laminae receive inter-laminar connections; Red, excitatory; blue, inhibitory. (B) Schematic of laminar IC slice plane. Top, Transverse brain slab with additional cuts to generate a laminar slab; Left panel, Direction of the two cuts (dashed lines) made in the transverse brain slab; the lower cut parallel to LL afferents and the upper cut parallel to the laminae; middle panel, orientation of the brain slab on the surface of the vibratome cutting plate. The slab is pushed down so that the bottom surface straightens out, generating a single plane containing LL afferents and the IC. Right panel, the laminar slice; Only one side of the IC is present. SC, superior colliculus; Stim, LL stimulating electrode; Bottom, The laminar slice plane contains LL input fibers synapsing on rows of disk-shaped neurons, and local circuitry; Red, excitatory; blue, inhibitory (Reprinted and adapted with permission from Springer).