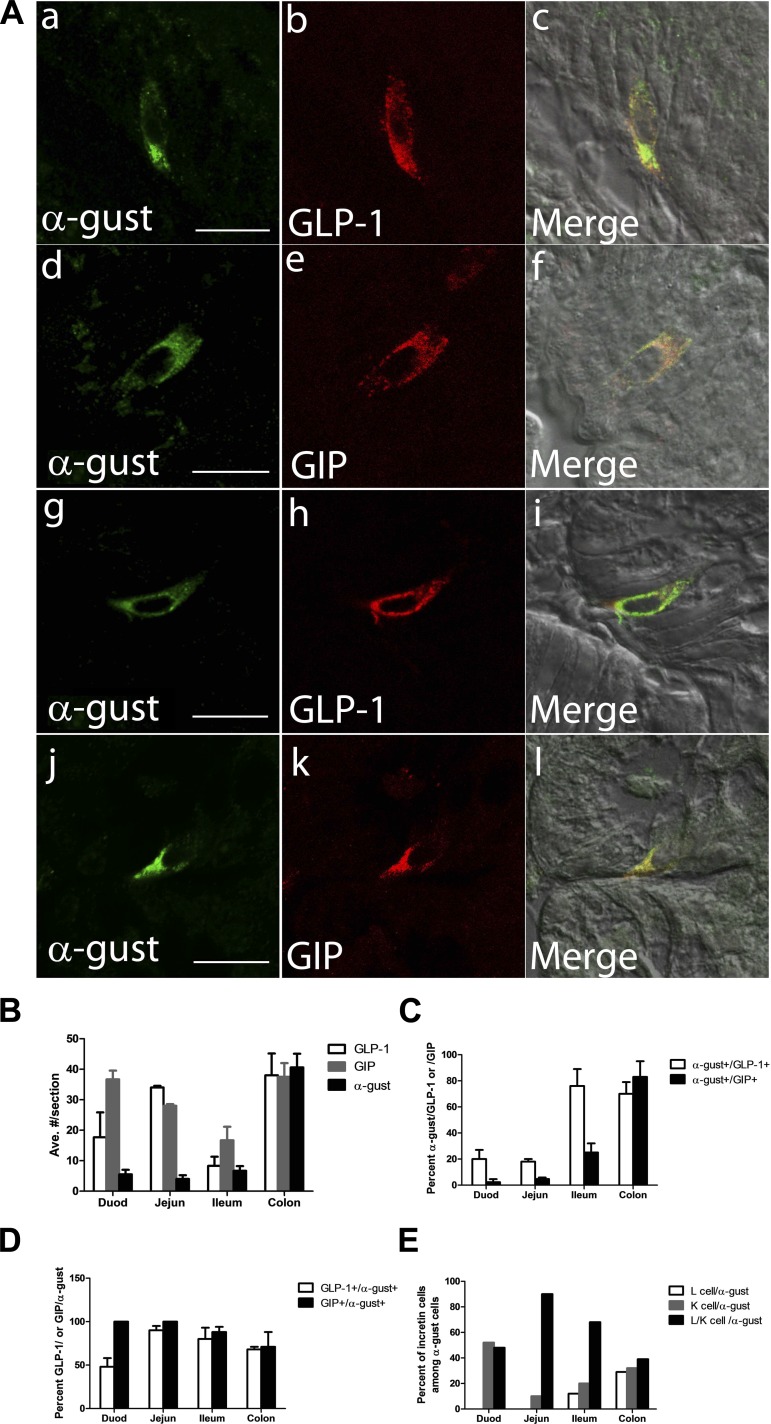
Fig. 1.
Coexpression of α-gustducin with glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) in small intestine and colon. A: indirect immunofluorescent confocal imaging showing coexpression of α-gustducin (α-gust) with GLP-1 and GIP in jejunum (a–f) and proximal colon (g–l) (scale bar, 16 μm). B: quantitation of cells positive for GLP-1, GIP, and α-gustducin in different segments of gut. C: percentage of GLP-1- or GIP-positive cells in mouse proximal colon coexpressing α-gustducin. Values are means ± SE from three sections. D: percentage of α-gustducin-positive cells in mouse proximal colon coexpressing GLP-1 or GIP. Values are means ± SE from three sections. E: calculation of α-gustducin distribution in enteroendocrine L (GLP-1+), K (GIP+), and L/K (GLP-1+/GIP+) cells. The calculation was based on the same data set used to generate Fig. 1D.