Figure 12.
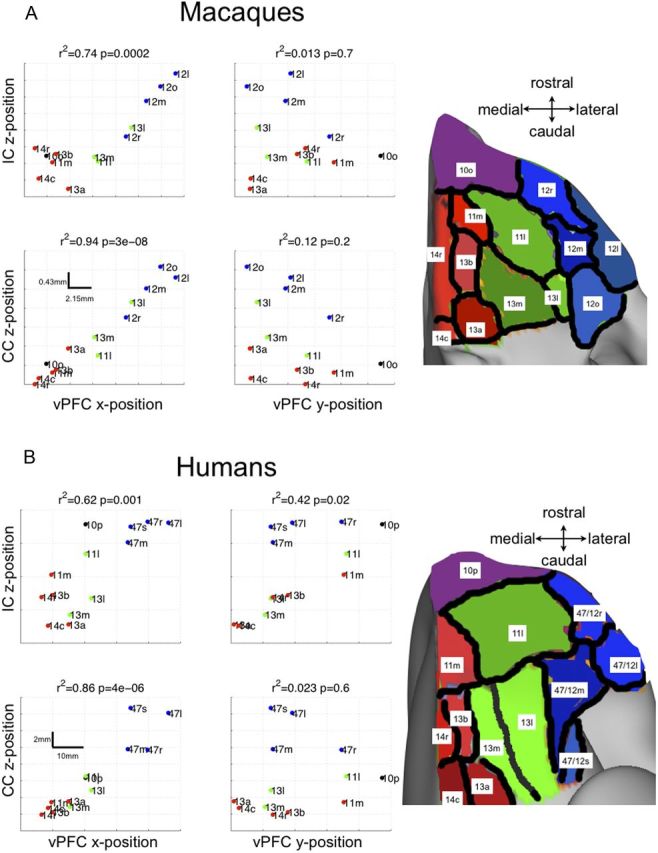
Macaque (A) and human (B) whole vPFC analysis of WM projections in the IC and CC. Left panel, The scatter plots show the positions of the centers of gravity of the vPFC seed regions plotted against the centers of gravity of the pathways. It is clear that the x-position (medial-lateral) of the seed regions correlates significantly with the z-position (ventral-dorsal) of the IC and CC projections (R2 statistics and p values shown on the plots). This is not the case for the y-position (rostrocaudal) of the seed regions. Right panel, Subdivision of the vPFC into 13 regions according to Carmichael and Price (1994) for macaques and (Ongur et al., 2003) for humans. The regions are colored in red/green/blue according to their approximate medial-dorsal positions for ease of visualization. Anterior regions 10o and 10p are colored differently because they span both medial and central positions. The nomenclature of the regions follows the convention adopted previously (Ongur et al., 2003). On the scatter plots (B), the subregions 47/12× are simply labeled 47×.
