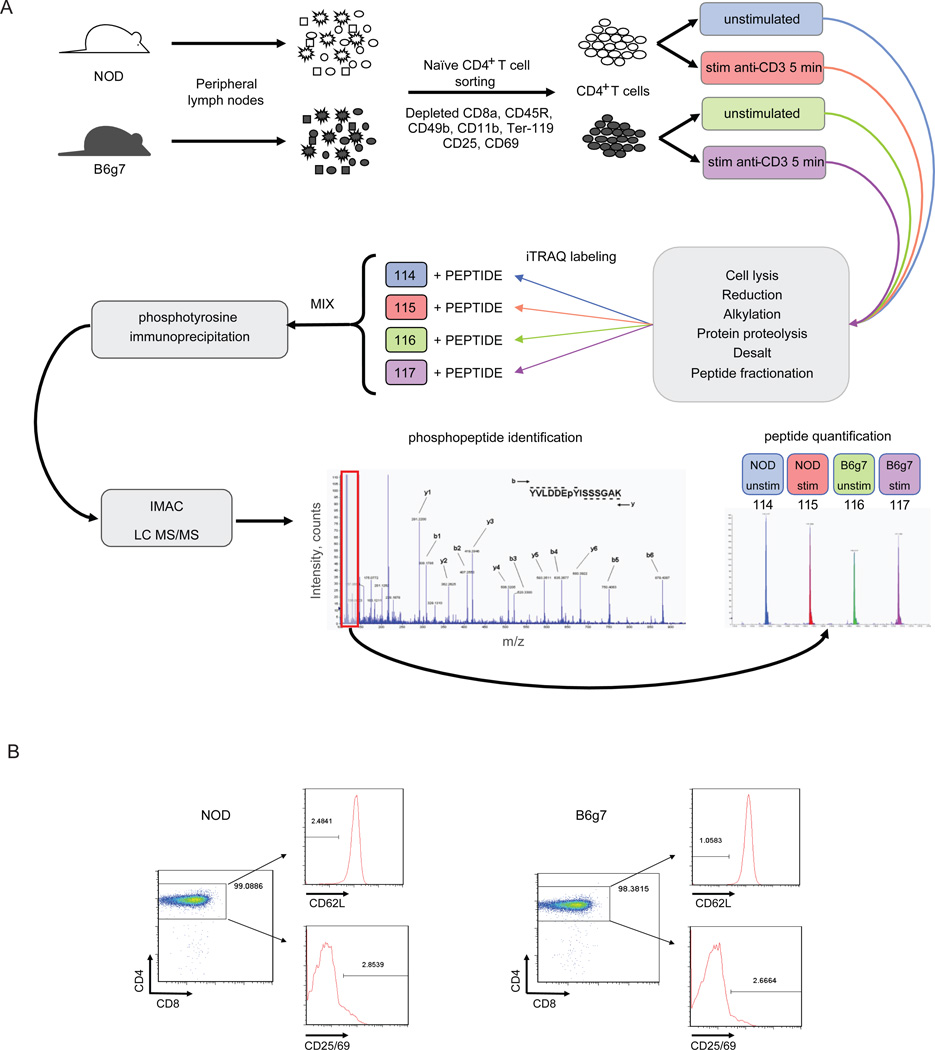
Figure 1.
A. Experimental scheme: subcutaneous lymph nodes were isolated from NOD and B6g7 mice and CD4+ T cells were magnetically separated by negative selection, thereby depleting non-CD4+ T cells using anti-CD8a, anti-CD45R, anti-CD49b, anti-CD11b and anti-Ter-119 to deplete CD8+ T cells, B cells, NK cells, macrophages, and erythroid cells, respectively. In addition preactivated or regulatory T cells were also depleted using anti-CD25 and anti-CD69 antibody. Half of the cells were left unstimulated and the other half was stimulated with anti-CD3 antibody for 5 min. Lysed cells were enzymatically digested, labeled separately with iTRAQ and combined. Upon phosphotyrosine enrichment by phosphotyrosine immunoprecipitation and IMAC, sample was subjected to LC-MS/MS analysis. Identification of each peptide was manually confirmed and quantification was performed by the analysis of the area from iTRAQ marker ions present in the MS/MS analysis. B. Assessment of CD4+ T cell separation analysis from both NOD and B6g7 subcutaneous lymph nodes by flow cytometry. CD4+ T cells separation were essentially >97%.