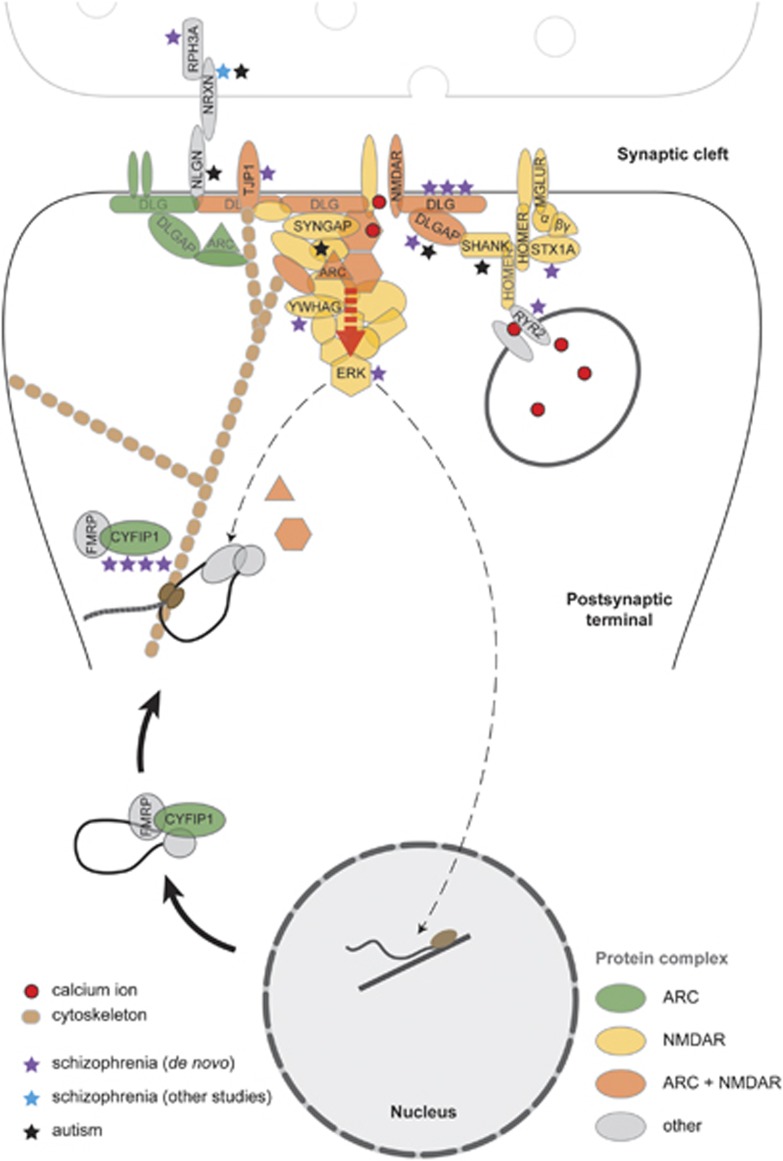
Figure 3.
Disruption of postsynaptic signalling within activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein (ARC) and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) complexes by copy number variants (CNVs). ARC and NMDAR bind to diverse structural and signalling molecules forming multiprotein complexes. Functional pathways encoded by these complexes are disrupted by de novo CNVs at multiple levels, as indicated by the purple asterisks (number of asterisks=number of de novos overlapping a gene or gene family). Calcium influx via the NMDAR, modulated by calcium release from internal stores (RYR2), drives downstream pathways whose association with the receptor is mediated by scaffold proteins (DLG1, DLG2, DLGAP1). Multiple pathways converge on ERK kinases (extracellular signal-regulated kinases), a focal point in the regulation of ARC transcription, dendritic localisation and local translation.47 ARC mRNA is transported to sites of synaptic activity in complexes containing CYFIP1, dissociation of which is required for ARC translation.49 CYFIP1 also regulates translation of CAMKII,49 a key component of NMDAR complexes. Although not identified in this study, deletions of synaptic adhesion protein NRXN1 (blue asterisk) have previously been found in schizophrenia.29 CNVs disrupting genes within these same functional pathways have also been identified in autism30(black asterisks).