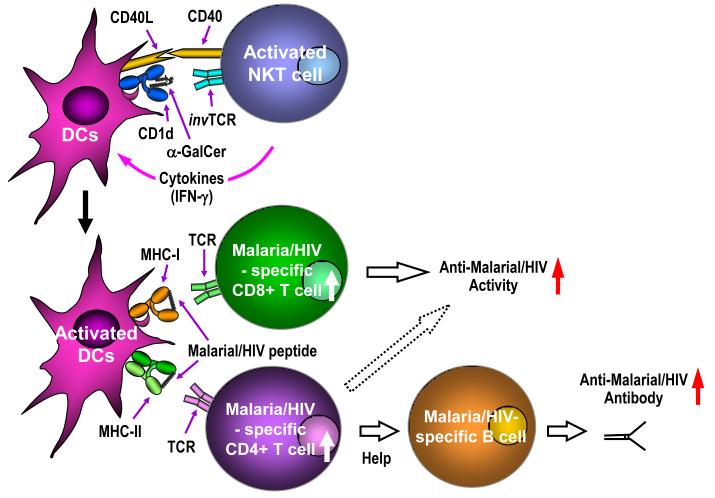
Figure 2.
Role of NKT cells in adaptive immunity against malaria and HIV. In the context of CD1d molecules, α-galactosyl ceramide (α-GalCer) stimulates NKT cells through their invariant T cell receptor (invTCR). Upon activation, NKT cells rapidly secrete cytokines such as IFN-γ, and together with CD40-CD40L interaction, induce activation and maturation of dendritic cells (DCs). Thus, co-administration of α-GalCer with vaccines expressing malaria or HIV antigens are able to enhance the efficacy of the vaccines by augmenting the levels of antigen-specific T cell and humoral responses.