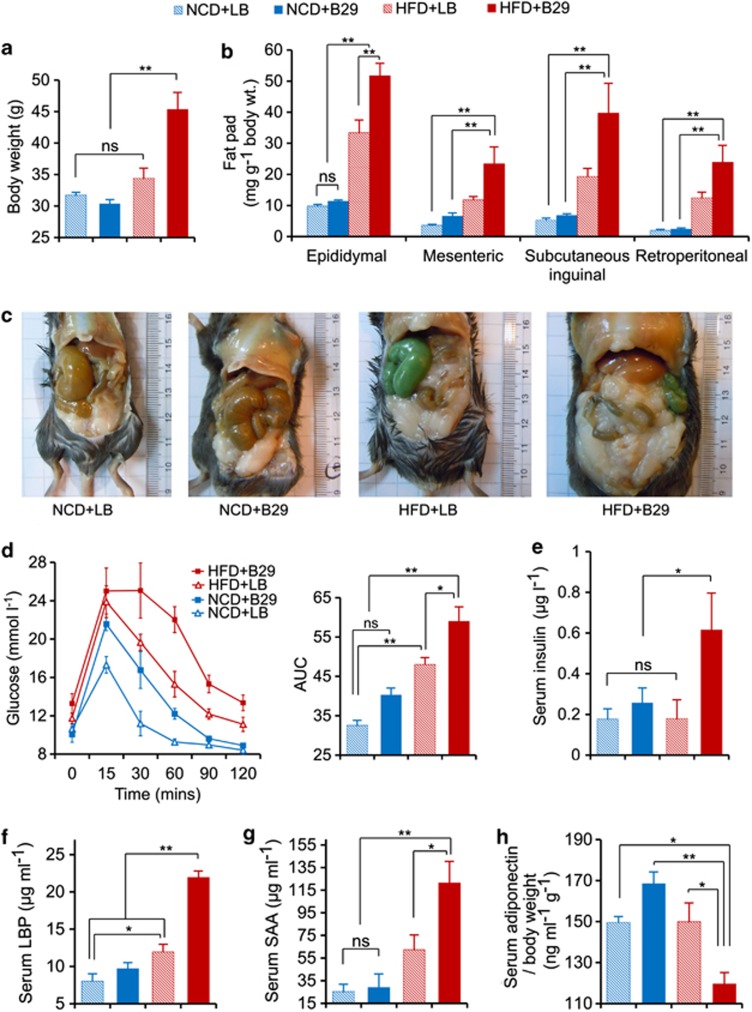
Figure 1.
Gnotobiotic mice mono-associated with E. cloacae B29 become obese and insulin resistant with increased endotoxin load and provoked systemic inflammation under HFD feeding (data collected at the end of 16 weeks after inoculation). (a) Body weight; (b) mass of epididymal, mesenteric, subcutaneous inguinal and retroperitoneal fat pad; (c) abdominal photographs; (d) oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) and the areas under the curve (AUC) for the plasma glucose; (e) serum 2 h post load insulin; (f) enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) analysis of serum LPS-binding protein (LBP); (g) serum amyloid A (SAA); and (h) adiponectin corrected for bodyweight. The two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) revealed a significant effect of the diet (P<0.01), a significant effect of B29 (P<0.01) and a significant diet × B29 interaction effect (P<0.01) on body weight, mass of epididymal, mesenteric, subcutaneous inguinal and retroperitoneal fat pad, serum LBP; a significant effect of the diet (P<0.01) and a significant effect of B29 (P<0.01) on OGTT; a significant effect of B29 (P<0.05) on serum 2 h post load insulin. Data are shown as means±s.e.m. (n=6). NS, no significant difference; *P<0.05; **P<0.01. Color code for animal groups: NCD+LB, blue slash; NCD+B29, blue; HFD+LB, red slash; HFD+B29, red. LB, Luria–Bertani medium.