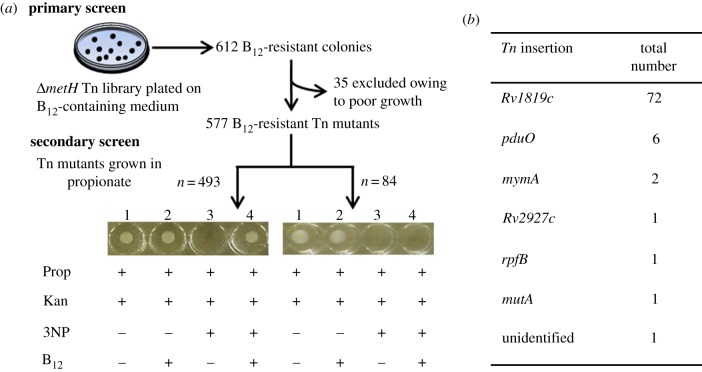
Figure 2.
Identification of genes required for B12 transport and assimilation. (a) Schematic of the screening cascade. The ΔmetH Tn library was plated on selective medium containing 10 µg ml−1 CNCbl. 612 ‘B12-resistant’ clones were isolated and regrown in standard liquid medium, eliminating 35 mutants owing to poor (n = 14) or absent (n = 21) growth. A secondary screen tested the B12 uptake ability of the remaining 577 insertion mutants in a four-well microtitre assay using 0.1% propionate (Prop) plus 20 µg ml−1 kanamycin as base medium (well 1) supplemented with 10 µg ml−1 CNCbl (well 2), 3NP (well 3) and 3NP plus 10 µg ml−1 CNCbl (well 4). A total of 84 mutants failed to grow in well 4, suggesting impaired B12 uptake. Each determination was performed in duplicate, and the results confirmed in batch culture. (b) Insertion mutants with disrupted B12 uptake ability.