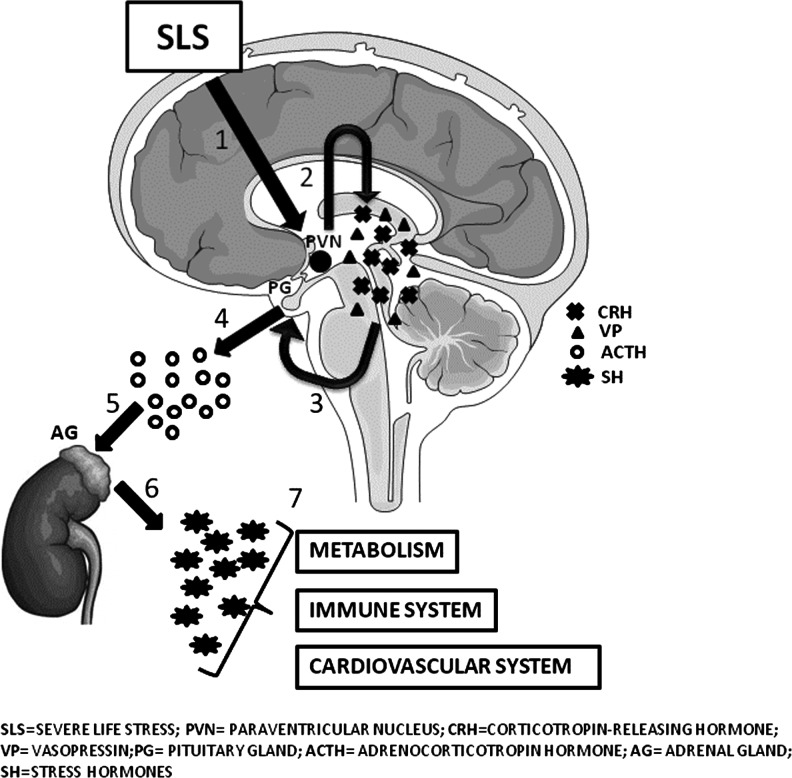
FIG. 2.
The HPA-axis functioning. After an SLS, an increase in the production of CRH and VP by the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus occurs. These two peptides mainly act on the anterior lobe of the PG, stimulating the secretion of the ACTH, which, in turn, acts on the cortices of adrenal glands. The main consequence of the stimulation of the adrenal cortices is the production of SH (mainly cortisol in humans), which is a key player in the regulation of metabolism (in particular, lipidic and glicemic metabolic pathways), the immune system, and cardiovascular functions. ACTH, adrenocorticotropic hormone; CRH, corticotropin-releasing hormone; HPA, hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal; SLS, severe life stress; VP, vasopressin.