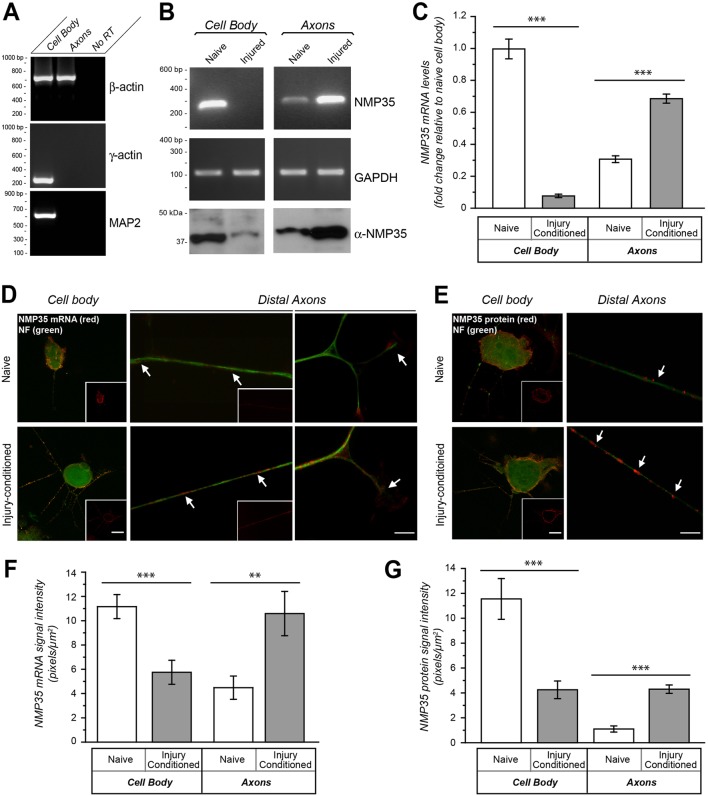
Fig. 1.
NMP35 mRNA and protein are enriched in axons of injury-conditioned neurons in culture. Dissociated DRG cultures prepared from naïve and injured rats at 7 days following sciatic nerve crush were used for fractionation of cell bodies and axons (A–C) or for FISH and immunofluorescence (D–G) after 24 hours in vitro. (A–C) By RT-PCR, β-actin was detected only in the axonal processes, but γ-actin and MAP2 mRNAs were restricted to the cell body samples showing purity of the axonal preparations (A). By both standard (B) and quantitative RT-PCR (C) NMP35 mRNA levels shift from cell body to axon predominance in the neurons from the injured animals. Amplification of GAPDH shows equivalent levels of total RNA in the standard RT-PCR; 12S rRNA was used for normalization of the RTqPCR. (D,E) By FISH (D) and immunofluorescence (E), both NMP35 mRNA and protein appear more abundant in the axons (arrows) and reduced in cell bodies of DRG neurons cultured from injury-conditioned compared with naïve animals. The cell body images in D and E show XYZ maximum projections constructed from 10 optical planes taken at 0.5 µm intervals; the inset panels show only the NMP35 mRNA or protein signals. (F,G) Quantification of FISH (F) and immunofluorescence (G) signals for axons and cell bodies from matched exposure images as in D and E are shown. All image pairs of naïve and injury-conditioned neurons are matched for exposure, gain, offset and post-processing (n≥15 for cell body and n≥20 for axons from at least three separate experiments; **P≤0.01, ***P≤0.001 by Student's t-test). Values in C, F and G are means±s.e.m. Scale bars: 10 µm for main panels, 50 μm for insets.